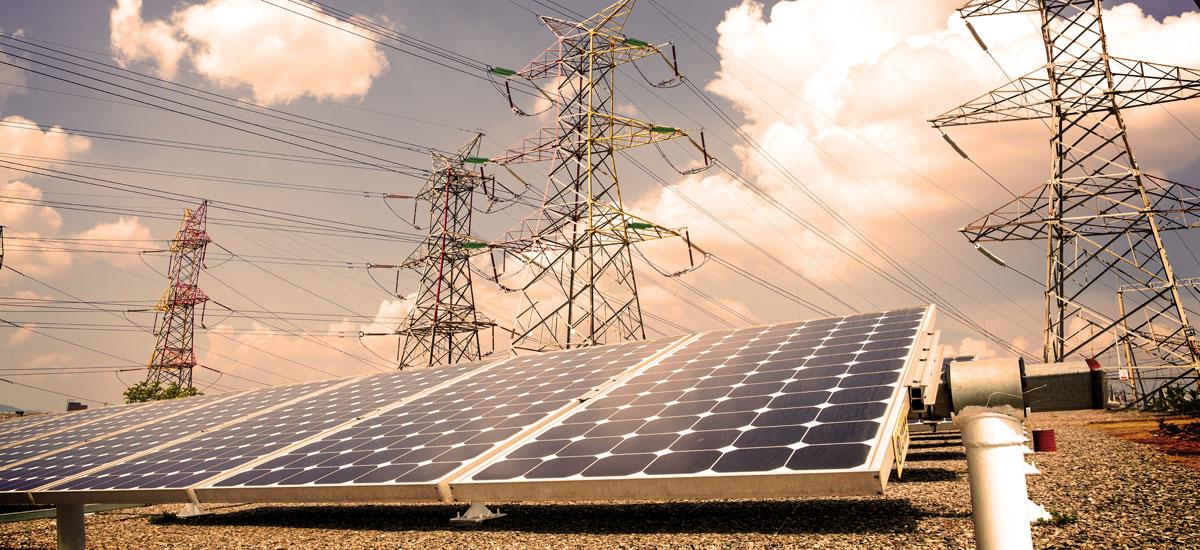
تجهیزات ایستگاههای تولید انرژی برق خورشیدی و چگونگی عملکرد سیستمهای تولید برق خورشیدی
Equipment of Solar Power Generation Stations and How Solar Power Systems Operate
*تمام حقوق این مقاله برای سازه گستر پایتخت محفوظ است
چکیده
این مقاله به بررسی تجهیزات و عملکرد سیستمهای تولید انرژی برق خورشیدی میپردازد. با توجه به نگرانیهای جهانی درباره تغییرات اقلیمی و نیاز روزافزون به منابع انرژی پایدار، انرژی خورشیدی به یک گزینه مطمئن و کارآمد تبدیل شده است. در این مقاله، در ابتدا به تجهیزات اصلی شامل پنلهای خورشیدی، اینورترها و سیستمهای مکانیکی اشاره میشود. سپس عملکرد این سیستمها و انواع آنها، بهویژه سیستمهای متصل به شبکه و غیرمتصل به شبکه، مورد بررسی قرار میگیرد. همچنین، تحلیل اقتصادی و مالی و چالشها و مزایای این سیستمها به همراه پیشرفتهای فناوری و سیاستهای دولتی بهمنظور حمایت از انرژی خورشیدی ارائه میشود. در پایان، به آینده انرژی خورشیدی و تحولات پیشبینیشده پرداخته میشود.
واژگان کلیدی
انرژی خورشیدی، پنلهای خورشیدی، سیستمهای فتوولتائیک، اینورتر خورشیدی، ذخیرهسازی انرژی، کاربردهای انرژی تجدیدپذیر، سیستمهای ردیاب خورشیدی، تحلیل اقتصادی انرژی، انرژی پاک، فناوریهای نوین خورشیدی
شما می توانید برای خرید و اطلاع از قیمت تجهیزات ایستگاههای تولید انرژی برق خورشیدی و پانل های خورشیدی مورد نیاز خود از طریق مشاوره با کارشناسان سازه گستر پایتخت اقدام نمایید.
گروه سازه گستر پایتخت با تکیه بر بیش از 20 سال تجربه و فعالیت به عنوان تامین کننده تجهیزات و ملزومات صنعت برق کشور ( الکتریکال - مکانیکال - ابزار دقیق ) با افتخار آماده خدمت رسانی به فعالان صنعت برق و صاحبان صنایع می باشد.
شماره تماس : 32 20 17 66 - 021
پست الکترونیک: info@sazehgostarsgp.com
نشانی: تهران، میدان فردوسی، کوچه گلپرور، پلاک 20، واحد25
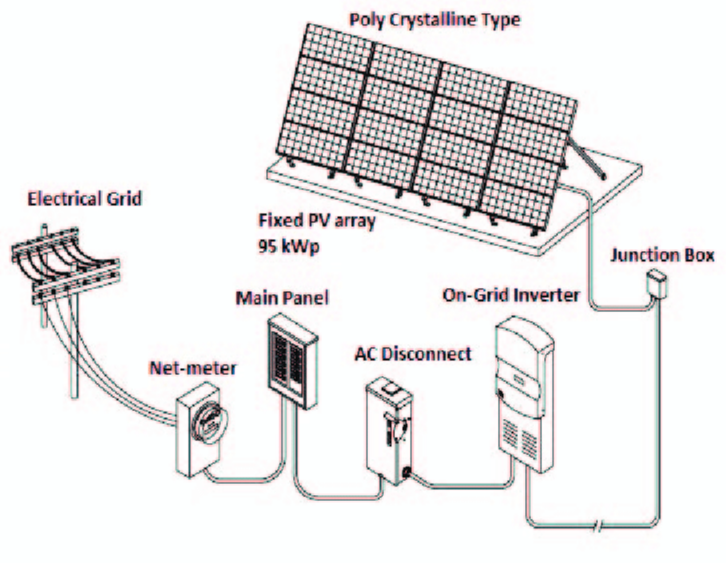
فصل 1: مقدمه
با افزایش سریع جمعیت و نیاز روزافزون به انرژی، تغییرات اقلیمی به یکی از بزرگترین چالشهای قرن بیست و یکم تبدیل شده است. سوختهای فسیلی، به عنوان منابع اصلی تولید انرژی، خطرات جدی را برای محیطزیست به همراه دارند و به افزایش دما و آلودگی هوا دامن میزنند. در این راستا، انرژی خورشیدی بهعنوان یکی از منابع تجدیدپذیر و پاک، در دهههای اخیر به طور فزایندهای مورد توجه قرار گرفته است.
نقاط قوت انرژی خورشیدی شامل دسترسی به منبع نور در اکثر مناطق، قابلیت نصب در مقیاسهای مختلف (از سیستمهای خانگی گرفته تا مزارع خورشیدی بزرگ) و هزینههای کاهشدهنده در تولید و نصب پنلها است. همچنین، استفاده از انرژی خورشیدی کمک میکند تا وابستگی به سوختهای فسیلی کاهش یابد.
با توجه به این عوامل، این مقاله تلاش میکند تا به بررسی دقیق تجهیزات مختلف ایستگاههای تولید انرژی برق خورشیدی و چگونگی عملکرد آنها بپردازد و نشان دهد که چگونه این سیستمها میتوانند در آینده انرژی پایدارتر و بهینهتر باشند.

فصل 2: تجهیزات اصلی ایستگاههای برق خورشیدی
2.1. پنلهای خورشیدی
پنلهای خورشیدی، که بهعنوان جمعکنندگان انرژی خورشیدی شناخته میشوند، از سلولهای فتوولتائیک تشکیل شدهاند. این سلولها بهطور عمده از سیلیکون ساخته شده و با جذب نور خورشید انرژی الکتریکی تولید میکنند.
- پنلهای مونوکریستالی: معمولاً بالاترین کارایی را دارند و میتوانند در فضاهای محدود به حداکثر تولید برق دست یابند. برخی از برندهای معتبر شامل:
- SunPower Maxeon: با کارایی بالای ۲۲ درصد.
- LG NeON 2: کارایی نزدیک به ۲۰.۳ درصد.
- پنلهای پلیکریستالی: هزینه کمتری نسبت به پنلهای مونوکریستالی دارند و در وضعیتی با نور کمتر نیز به خوبی کار میکنند. برندهای معروف شامل:
- Canadian Solar: کیفیت بالا و قیمت مناسب.
- Trina Solar: یکی از بزرگترین تولیدکنندگان در سطح جهانی با کارایی بالا.
- پنلهای فیلم نازک: در مقایسه با نوعهای دیگر، سبکتر و منعطفتر هستند. از جمله برندهای معتبر در این زمینه میتواند به First Solar اشاره کرد.
2.2. اینورترها
اینورترها وظیفه دارند جریان مستقیم (DC) تولیدی توسط پنلها را به جریان متناوب (AC) تبدیل کنند که برای استفاده در شبکه برق عمومی یا مصرف خانگی لازم است.
اینورترهای متصل به شبکه: بهطور همزمان با شبکه کار کرده و انرژی تولیدی را به شبکه برمیگردانند. برندهای معتبر شامل:
- SMA Sunny Boy: با پشتیبانی قوی و کیفیت بالا.
- Fronius Primo: یکی از پیشرفتهترین اینورترها با منوی کاربر پسند.
اینورترهای غیرمتصل به شبکه: بیشتر در سیستمهای مستقل استفاده میشوند، مانند:
- OutBack FXR: برای کاربردهای نوسانی و مقاوم به بارندگی.
- Renogy inverter: مناسب برای تولید برق مستقل.
2.3. سیستمهای مکانیکی و ساختاری
این گروه شامل سازههایی است که پنلهای خورشیدی بر روی آنها نصب میشوند. سیستمهای ردیاب خورشیدی نیز در این دسته قرار میگیرند:
- سیستمهای ردیاب یکمحوری: این سیستمها فقط در یک محور حرکت میکنند و معمولاً در عرضی نصب میشوند.
- سیستمهای ردیاب دو محوری: این سیستمها قادرند در دو محور حرکت کنند و بالاترین کارایی را در جذب نور خورشید با توجه به موقعیت خورشید در آسمان دارند.
- Array Technologies و NEXTracker از جمله برندهای معتبر در تولید سیستمهای ردیاب خورشیدی هستند.
مطالعه مقاله: تجهیزات ایستگاههای انتقال برق فشار قوی در کلانشهرها
ایستگاههای انتقال برق فشار قوی به عنوان قلب شبکههای برقرسانی، نقش حیاتی در انتقال انرژی الکتریکی از تولیدکنندگان به مصرفکنندگان ایفا میکنند. با رشد جمعیت و توسعه زیرساختهای شهری، اهمیت این ایستگاهها در کلانشهرها دوچندان گردیده است. این مقاله به بررسی تجهیزات مختلف ایستگاههای انتقال برق فشار قوی در کلانشهرها، چالشهای موجود، و راهکارهایی برای مواجهه با این چالشها میپردازد... ادامه مطلب
فصل 3: عملکرد سیستمهای تولید برق خورشیدی
3.1. فرآیند تولید برق
وقتی نور خورشید به سلولهای فتوولتائیک میتابد، الکترونها به حرکت درمیآیند و انرژی الکتریکی تولید میشود. این فرآیند بهعنوان اثر فتوولتائیک شناخته میشود. هر سلول شامل دو لایه سیلیکون با ترکیبات مختلف است که باعث ایجاد یک میدان الکتریکی میشود. این میدان، الکترونها را به سمت یک طرف کشیده و انرژی الکتریکی تولید میکند.
3.2. ذخیرهسازی انرژی
ذخیرهسازی انرژی در سیستمهای خورشیدی از اهمیت بالایی برخوردار است. باتریها بهعنوان واحدهای ذخیرهسازی عمل میکنند و این امکان را فراهم میکنند که انرژی تولیدی در روز برای استفاده در شب یا روزهای ابری ذخیره شود.
- فناوریهای مختلفی برای ذخیرهسازی انرژی وجود دارد، که شامل باتریهای لیتیم-یونی، نیکل-کادمیوم و باتریهای نوین مانند باتریهای حالت جامد است. برخی از برندهای معتبر شامل:
- Tesla Powerwall: برای ذخیره انرژی خانگی.
- LG Chem RESU: باتریهای خانگی با ظرفیت بالا.
فصل 4: بررسی سیستمهای خورشیدی متصل به شبکه
4.1. تعاریف و ویژگیها
سیستمهای خورشیدی متصل به شبکه به تجهیزات عمومی شناخته میشوند که به شبکه برق متصل شده و امکان تولید انرژی و فروش مازاد آن به شبکه را فراهم میکنند. این سیستمها به کاربران اجازه میدهند تا از مزایای کار کردن با شبکه برق محلی بهرهمند شوند.
4.2. مزایا
- کاهش هزینههای انرژی: تولید برق بهوسیله پنلهای خورشیدی میتواند هزینههای انرژی را کاهش دهد و در برخی موارد به صفر برساند.
- فروش به شبکه: کاربران میتوانند انرژی اضافی خود را به شبکه بفروشند و درآمدی برای خود کسب کنند.
- استفاده از فناوری هوشمند: قابلیت ردیابی دادهها و برنامهریزی مصرف انرژی.
4.3. چالشها
- نوسانات تولید: تولید انرژی خورشیدی به آب و هوا وابسته است و ممکن است در شرایط ابرناکی یا بارانی کاهش یابد.
- نیاز به فضای کافی: نصب پنلها به فضای فیزیکی نیاز دارد که میتواند برای برخی کاربران چالشبرانگیز باشد.
- سرمایهگذاری اولیه: هزینههای بالای نصب و تأسیس ممکن است برای برخی کاربران محدودیت ایجاد کند.
مطالعه مقاله: انواع تابلوهای برق صنعتی فشار قوی و تجهیزات آن
تابلوهای برق صنعتی فشار قوی به عنوان اجزای کلیدی در سیستمهای توزیع برق، نقش حیاتی در کنترل و توزیع انرژی الکتریکی ایفا میکنند. این تابلوها به دلیل ولتاژ بالای کارکرد، نیاز به طراحی و ساخت ویژهای دارند تا ایمنی و کارایی سیستم برق را تضمین کنند. در این مقاله، به بررسی انواع تابلوهای برق فشار قوی، تجهیزات مرتبط، کاربردها و نکات ایمنی پرداخته میشود... ادامه مطلب

فصل 5: بررسی سیستمهای خورشیدی غیرمتصل به شبکه
5.1. تعاریف و کاربردها
سیستمهای غیرمتصل به شبکه بهویژه در مناطق دورافتاده و روستاها کاربرد دارند که امکان دسترسی به شبکه برق عمومی وجود ندارد. این سیستمها شامل پنلهای خورشیدی، اینورتر و باتری هستند و بهعنوان منبع مستقل انرژی عمل میکنند.
5.2. مزایا
- منبع انرژی مستقل: تأمین انرژی در مناطقی که به شبکه برق دسترسی ندارند.
- کاهش وابستگی به سوختهای فسیلی: استفاده از انرژی خورشیدی به کاهش وابستگی به منابع نفت و گاز کمک میکند.
- کاهش اثرات زیستمحیطی منفی: این آسیابها به حفظ محیط زیست کمک میکنند.
5.3. چالشها
- هزینههای نصب بالا: نصب این نوع سیستمها ممکن است هزینهبر باشد.
- نیاز به نگهداری منظم: برای عملکرد بهینه، این سیستمها نیاز به نگهداری و سرویس منظم دارند.
- محدودیت در ظرفیت ذخیرهسازی: ظرفیت باتریهای موجود ممکن است کافی نباشد و در برخی موارد تولید انرژی مور نیاز را تأمین نکند.

فصل 6: تحلیل اقتصادی و مالی سیستمهای انرژی خورشیدی
تحلیلهای اقتصادی این سیستمها نشان میدهند که اگرچه هزینههای اولیه نصب ممکن است بالا باشد، اما صرفهجویی در هزینههای برق در طول زمان موجب بازگشت سرمایه خواهد شد.
6.1. هزینههای اولیه و جاری
- هزینه نصب: شامل پنلها، اینورتر، باتری، و هزینههای کارگری.
- هزینههای جاری: نگهداری، تعمیرات و بروز رسانی تجهیزات.
6.2. درآمدزایی
- فروش انرژی به شبکه: در برخی کشورها، طرحهای تشویقی برای فروش انرژی اضافی به شبکه وجود دارد.
- صرفهجویی در هزینههای برق: کاهش هزینههای انرژی به لحاظ اقتصادی قابل توجه است.
فصل 7: آینده انرژی خورشیدی
آینده انرژی خورشیدی تحت تأثیر پیشرفتهای تکنولوژیکی و تغییرات سیاستهای دولتی خواهد بود.
7.1. تحولات فناوری
- پنلهای خورشیدی پیشرفته: توسعه پنلهای با کارایی بالاتر و هزینه کمتر.
- باتریهای نوین: فناوریهای جدید در ذخیرهسازی انرژی که به بهبود سیستمهای خورشیدی کمک میکند.
7.2. سیاستهای دولتی
- حمایت از انرژیهای تجدیدپذیر: سیاستهای تشویقی مثل کمکهای مالی و معافیتهای مالیاتی.
- برنامههای توسعه پایدار: تمرکز بر گسترش زیرساختهای انرژی خورشیدی در مقیاس بزرگ.
Equipment of Solar Power Generation Stations and How Solar Power Systems Operate
Abstract
This article examines the equipment and functioning of solar power generation systems. Given the global concerns about climate change and the increasing need for sustainable energy sources, solar energy has become a reliable and efficient option. Initially, the article discusses essential equipment, including solar panels, inverters, and mechanical systems. It then explores the operation of these systems and their various types, particularly grid-connected and off-grid systems. Additionally, the economic and financial analysis, along with the challenges and benefits of these systems, is presented, along with technological advancements and government policies aimed at supporting solar energy. Finally, the future of solar energy and anticipated developments are discussed
Keywords
Solar energy
Solar panels
Photovoltaic systems
Solar inverters
Energy storage
Renewable energy applications
Solar tracking systems
Energy economic analysis
Clean energy
Innovative solar technologies
Chapter 1: Introduction
With the rapid increase in population and growing demand for energy, climate change has become one of the significant challenges of the 21st century. Fossil fuels, as the primary sources of energy production, pose serious risks to the environment and contribute to rising temperatures and air pollution. In this context, solar energy has emerged as one of the renewable and clean sources increasingly receiving attention in recent decades
The strengths of solar energy include access to sunlight in most regions, the ability to be installed at various scales (from residential systems to large solar farms), and decreasing costs in the production and installation of panels. Moreover, using solar energy helps reduce dependence on fossil fuels
Considering these factors, this article aims to conduct a thorough examination of the various equipment used in solar power generation stations and how these systems operate, highlighting how they can contribute to a more sustainable and optimized energy future
Chapter 2: Main Equipment of Solar Power Stations
2.1. Solar Panels
Solar panels, also known as solar collectors, consist of photovoltaic cells. These cells are primarily made of silicon and generate electrical energy by absorbing sunlight
- Monocrystalline panels: They typically have the highest efficiency and can achieve maximum power generation in limited space. Notable brands include:
- SunPower Maxeon: With an efficiency of over 22%
- LG NeON 2: Efficiency close to 20.3%
- Polycrystalline panels: They are generally less expensive than monocrystalline panels and perform well in low-light conditions. Known brands include:
- Canadian Solar: High quality at a reasonable price
- Trina Solar: One of the largest manufacturers globally with high efficiency
- Thin-film panels: Compared to other types, they are lighter and more flexible. Notable brands in this area include First Solar
2.2. Inverters
Inverters are responsible for converting the direct current (DC) generated by the panels into alternating current (AC) necessary for use in the public electricity grid or household consumption.
Grid-tied inverters: These operate simultaneously with the grid, allowing users to feed excess energy back into it. Reputable brands include:
- SMA Sunny Boy: Known for strong support and high quality.
- Fronius Primo: One of the most advanced inverters with a user-friendly interface.
Off-grid inverters: More commonly used in independent systems, such as:
- OutBack FXR: Suitable for variable applications and rain-resistant
- Renogy inverter: Designed for off-grid energy production
2.3. Mechanical and Structural Systems
This category includes the structures on which solar panels are installed. Solar tracking systems are also included:
- Single-axis tracking systems: These systems move on one axis and are usually installed horizontally
- Dual-axis tracking systems: These systems can move on two axes, maximizing energy absorption based on the sun's position in the sky
- Array Technologies and NEXTracker are respected brands in solar tracking systems
Chapter 3: Operation of Solar Power Generation Systems
3.1. Electricity Generation Process
When sunlight strikes photovoltaic cells, electrons start to move, generating electrical energy. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect. Each cell consists of two layers of silicon with different doping that creates an electric field. This field draws electrons toward one side, producing electrical energy
3.2. Energy Storage
Energy storage in solar systems is crucial. Batteries serve as storage units, allowing the energy generated during the day to be used at night or on cloudy days
- Various technologies exist for energy storage, including lithium-ion, nickel-cadmium batteries, and innovative new technologies like solid-state batteries. Notable brands include:
- Tesla Powerwall: For household energy storage
- LG Chem RESU: High-capacity home batteries
Chapter 4: Analysis of Grid-Connected Solar Systems
4.1. Definitions and Features
Grid-connected solar systems are commonly recognized equipment that connects to the electrical grid, allowing the generation of energy and the possibility of selling excess energy back to the grid. These systems enable users to benefit from working with the local electricity grid
4.2. Advantages
- Reduction in energy costs: Solar panel-generated electricity can lower energy bills and, in some cases, bring them to zero
- Selling to the grid: Users can sell their excess energy to the grid, generating additional income
- Use of smart technology: The ability to track data and plan energy consumption
4.3. Challenges
- Production fluctuations: Solar energy production depends on weather conditions and may decrease under cloudy or rainy circumstances.
- Need for adequate space: Installing panels requires physical space, which can pose a challenge for some users
- Initial investment: High installation and setup costs may represent a limitation for some users
Chapter 5: Analysis of Off-Grid Solar Systems
5.1. Definitions and Applications
Off-grid systems are particularly useful in remote areas and villages where access to the public electricity grid is unavailable. These systems include solar panels, inverters, and batteries, functioning as independent energy sources
5.2. Advantages
- Independent energy source: Providing energy in areas with no access to power grids
- Reduction of dependence on fossil fuels: Utilizing solar energy helps diminish reliance on oil and gas resources
- Mitigating negative environmental impacts: These systems contribute to environmental preservation
5.3. Challenges
- High installation costs: Setting up these types of systems can be expensive
- Need for regular maintenance: Optimal performance requires regular maintenance and servicing
- Limitations in storage capacity: The capacity of available batteries may not always meet energy production needs
Chapter 6: Economic and Financial Analysis of Solar Energy Systems
Economic analyses of these systems show that, although initial installation costs may be high, savings on energy costs over time will ensure return on investment
6.1. Initial and Ongoing Costs
- Installation costs: Including panels, inverters, batteries, and labor costs
- Ongoing costs: Maintenance, repairs, and equipment upgrades
6.2. Revenue Generation
- Selling energy back to the grid: Some countries have incentive programs for selling surplus energy to the grid
- Savings on electricity bills: Reducing energy costs can be economically significant
Chapter 7: The Future of Solar Energy
The future of solar energy will be influenced by technological advancements and changes in government policies
7.1. Technological Developments
- Advanced solar panels: Development of higher efficiency panels at lower costs
- Innovative batteries: New technologies in energy storage that enhance solar systems
7.2. Government Policies
- Support for renewable energy: Incentive policies such as financial aid and tax exemptions.
- Sustainable development programs: Focus on expanding solar energy infrastructure on a large scale
References
Boyle, G. (2012). Renewable energy: Power for a sustainable future (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press.
Walker, A. (2018). Solar energy: Technologies and project delivery for buildings. Routledge.
Solar Energy International. (2017). Photovoltaics: Design and installation manual. New Society Publishers.
Boxwell, M. (2021). Solar electricity handbook: A simple, practical guide to solar energy – designing and installing solar photovoltaic systems. Green Stream Publishing.
Baird, D. B. (2010). Energy from the sun: Solar power technology. New Society Publishers.
Boxwell, M. (2021). The solar electricity handbook - 2021 edition: A simple, practical guide to solar energy – designing and installing solar photovoltaic systems. Green Stream Publishing.
Mugdad, A. J. (2019). Solar photovoltaics: Fundamentals, technology, and practice. Nova Science Publishers.
Colby, L. M. H. (2020). The new solar system: 300+ ways to go solar. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform.
Duffie, J. A., & Beckman, W. A. (2013). Solar engineering of thermal processes (4th ed.). Wiley.
Markvart, T., & Ferreira, L. C. (2012). Solar energy: The physics and engineering of photovoltaic conversion, technologies, and systems. Wiley.









