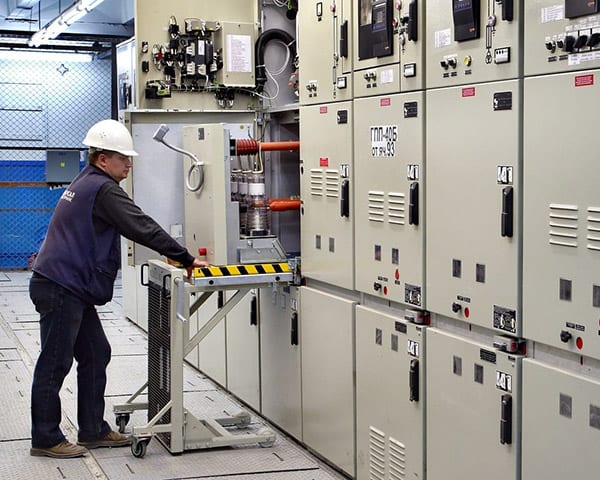
انواع تابلوهای برق صنعتی فشار قوی و تجهیزات آن
Types of High Voltage Industrial Electrical Panels and Their Equipment
*تمام حقوق این مقاله برای سازه گستر پایتخت محفوظ است
مقدمه
تابلوهای برق صنعتی فشار قوی به عنوان اجزای کلیدی در سیستمهای توزیع برق، نقش حیاتی در کنترل و توزیع انرژی الکتریکی ایفا میکنند. این تابلوها به دلیل ولتاژ بالای کارکرد، نیاز به طراحی و ساخت ویژهای دارند تا ایمنی و کارایی سیستم برق را تضمین کنند. در این مقاله، به بررسی انواع تابلوهای برق فشار قوی، تجهیزات مرتبط، کاربردها و نکات ایمنی پرداخته میشود.
شما می توانید برای خرید و اطلاع از قیمت انواع تجهیزات برق صنعتی فشار قوی مورد نیاز خود از طریق مشاوره با کارشناسان سازه گستر پایتخت اقدام نمایید.
گروه سازه گستر پایتخت با تکیه بر بیش از 20 سال تجربه و فعالیت به عنوان تامین کننده تجهیزات و ملزومات صنعت برق کشور ( الکتریکال - مکانیکال - ابزار دقیق ) با افتخار آماده خدمت رسانی به فعالان صنعت برق و صاحبان صنایع می باشد.
شماره تماس : 32 20 17 66 - 021
پست الکترونیک: info@sazehgostarsgp.com
نشانی: تهران، میدان فردوسی، کوچه گلپرور، پلاک 20، واحد 25

1. تعریف تابلو برق فشار قوی
تابلو برق فشار قوی به محفظههای فلزی اشاره دارد که تجهیزات الکتریکی برای کنترل، حفاظت و توزیع برق در آنها نصب میشود. این تابلوها معمولاً برای ولتاژهای بالای 63 کیلو ولت طراحی میشوند و در صنایع بزرگ، ایستگاههای برق و شبکههای توزیع مورد استفاده قرار میگیرند.
2. انواع تابلوهای برق فشار قوی
تابلوهای برق فشار قوی را میتوان بر اساس چندین معیار تقسیمبندی کرد:
از نظر ساختار:
- تابلو برق Metal Enclosed: این نوع تابلوها دارای محفظه فلزی هستند که به طور کامل تجهیزات داخلی را از عوامل محیطی محافظت میکند. این تابلوها معمولاً برای کاربردهای عمومی مناسب هستند.
- تابلو برق Metal Clad: این تابلوها دارای محفظههای جداگانه برای کلیدها، بریکرها و سایر تجهیزات هستند. این طراحی ایمنی بیشتری را فراهم میکند و خطرات ناشی از اتصال کوتاه را کاهش میدهد.
- تابلو برق Compartment Type: این تابلوها شامل محفظههای متصل به هم هستند که برای کاهش هزینهها و پیچیدگی طراحی شدهاند، ولی باید همچنان ایمنی را حفظ کنند.
- تابلو برق کشویی (Withdrawable): این نوع تابلوها به اپراتورها این امکان را میدهند که تجهیزات را به راحتی به بیرون بکشند و تعمیر و نگهداری آسانتری داشته باشند. این تابلوها معمولاً در محیطهای صنعتی بزرگ استفاده میشوند.
- تابلو برق گازی (GIS): استفاده از گاز SF6 به عنوان عایق در این تابلوها، امکان طراحی جمع و جور و ایمن را فراهم میکند. GIS برای کاربردهای ولتاژ بالا و در فضاهای محدود ایدهآل است.
از نظر ولتاژ:
- تابلو برق ولتاژ پایین (LV): این تابلوها برای ولتاژهای تا 1 کیلو ولت طراحی شدهاند و بیشتر در کاربردهای توزیع برق عمومی استفاده میشوند.
- تابلو برق ولتاژ متوسط (MV): این تابلوها برای ولتاژهای بین 1 تا 36 کیلو ولت طراحی شدهاند و در صنایع مختلف، از جمله پتروشیمی و تولید برق، کاربرد دارند.
- تابلو برق ولتاژ قوی (HV): این تابلوها بالای 36 کیلو ولت کار میکنند و معمولاً در ایستگاههای برق و شبکههای توزیع بزرگ به کار میروند.
مطالعه مقاله :
آخرین تکنولوژیهای برق صنعتی فشار قوی

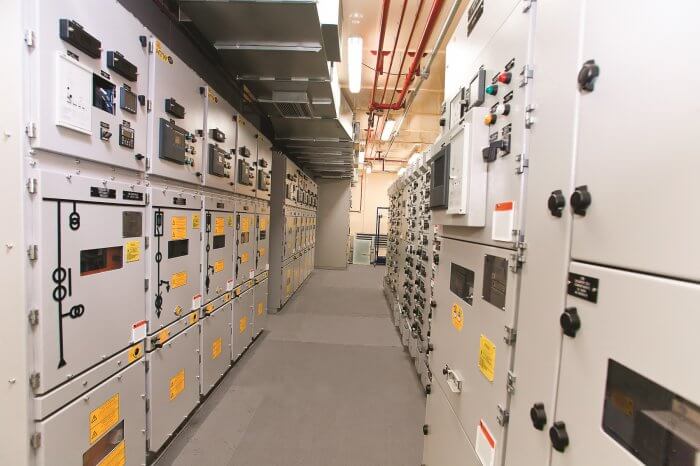
3. تجهیزات تابلو برق فشار قوی
تجهیزات مختلفی در تابلوهای برق فشار قوی وجود دارد که هر کدام وظایف خاصی را بر عهده دارند:
مدار شکنها (Circuit Breakers):
- مدار شکنهای مینیاتوری (MCB): برای حفاظت در برابر اضافه بار و اتصال کوتاه در مدارهای کمولتاژ استفاده میشوند.
- مدار شکنهای خودکار (Automatic Circuit Breakers): برای حفاظت از بارهای بزرگ در سیستمهای فشار قوی طراحی شدهاند.
- برندهای معتبر: Schneider Electric, Siemens, ABB.
ترانسفورماتورها:
- ترانسفورماتورهای توزیع: برای تبدیل ولتاژ در سیستمهای توزیع استفاده میشوند.
- ترانسفورماتورهای قدرت: برای انتقال انرژی در ولتاژهای بالا به کار میروند.
- برندهای معتبر: General Electric (GE), Siemens, Mitsubishi Electric.
کابلها:
- کابلهای فشار قوی: برای انتقال جریان الکتریکی در ایستگاههای برق و تابلوها استفاده میشوند.
- کابلهای عایق شده: برای حفاظت در برابر خطرات الکتریکی.
- برندهای معتبر: Nexans, Prysmian Group, Southwire.
فیوزها:
- فیوزهای قدرت: برای حفاظت از تجهیزات در برابر اضافه بار و اتصال کوتاه.
- فیوزهای سریع: برای حفاظت از بارهای حساس.
- برندهای معتبر: Eaton, Littelfuse, Bussmann.
کنتاکتورها:
- کنتاکتورهای AC و DC: برای کنترل روشن و خاموش کردن موتورها و تجهیزات.
- برندهای معتبر: Siemens, Schneider Electric, Allen-Bradley.
رلههای حفاظتی:
- رلههای حفاظتی دیجیتال: برای نظارت بر شرایط الکتریکی و تشخیص خطاها.
- رلههای حرارتی: برای حفاظت از موتورهای الکتریکی.
- برندهای معتبر: SEL (Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories), ABB, GE.
مطالعه مقاله:
سکسیونرها در سیستمهای برق فشار قوی: کاربردها، عملکرد و اهمیت
4. کاربردهای تابلو برق فشار قوی
تابلوهای برق فشار قوی در صنایع مختلف کاربرد دارند، از جمله:
توزیع برق در صنایع بزرگ:
- این تابلوها برای توزیع انرژی الکتریکی به تجهیزات و ماشینآلات سنگین در صنایع پتروشیمی، فولاد و معدن استفاده میشوند. به عنوان مثال، در کارخانههای فولادسازی بزرگ مانند کارخانه فولاد Tata Steel در هند، تابلوهای فشار قوی برای مدیریت و توزیع برق به ماشینآلات تولید و فرآوری استفاده میشوند.
کنترل و حفاظت از موتورهای الکتریکی:
- تابلوهای فشار قوی برای کنترل و حفاظت از موتورهای الکتریکی در فرآیندهای صنعتی مانند پمپها و کمپرسورها به کار میروند. برای نمونه، در تأسیسات نفتی مانند Offshore Oil Platforms، تابلوهای برق فشار قوی برای تأمین برق موتورهای پمپ و تجهیزات دیگر ضروری هستند.
ایستگاههای برق و شبکههای توزیع:
- این تابلوها در ایستگاههای برق برای مدیریت و توزیع انرژی الکتریکی به مناطق مختلف به کار میروند. به طور مثال، ایستگاههای برق Hoover Dam در ایالات متحده، از تابلوهای فشار قوی برای کنترل توزیع انرژی حاصل از سد استفاده میکنند.
سیستمهای انرژی تجدیدپذیر:
- در پروژههای انرژی خورشیدی و بادی، تابلوهای برق فشار قوی برای مدیریت و توزیع انرژی تولید شده ضروری هستند. برای مثال، در پارکهای خورشیدی مانند Solar Star در کالیفرنیا، تابلوهای فشار قوی برای اتصال به شبکه برق ملی و کنترل جریان برق استفاده میشوند.
تأسیسات زیرزمینی:
- در معادن و تأسیسات زیرزمینی، تابلوهای فشار قوی برای تأمین برق و کنترل تجهیزات استفاده میشوند. به عنوان نمونه، در معدن Grasberg در اندونزی، تابلوهای برق فشار قوی برای تأمین برق تجهیزات سنگین و سیستمهای تهویه استفاده میشود.
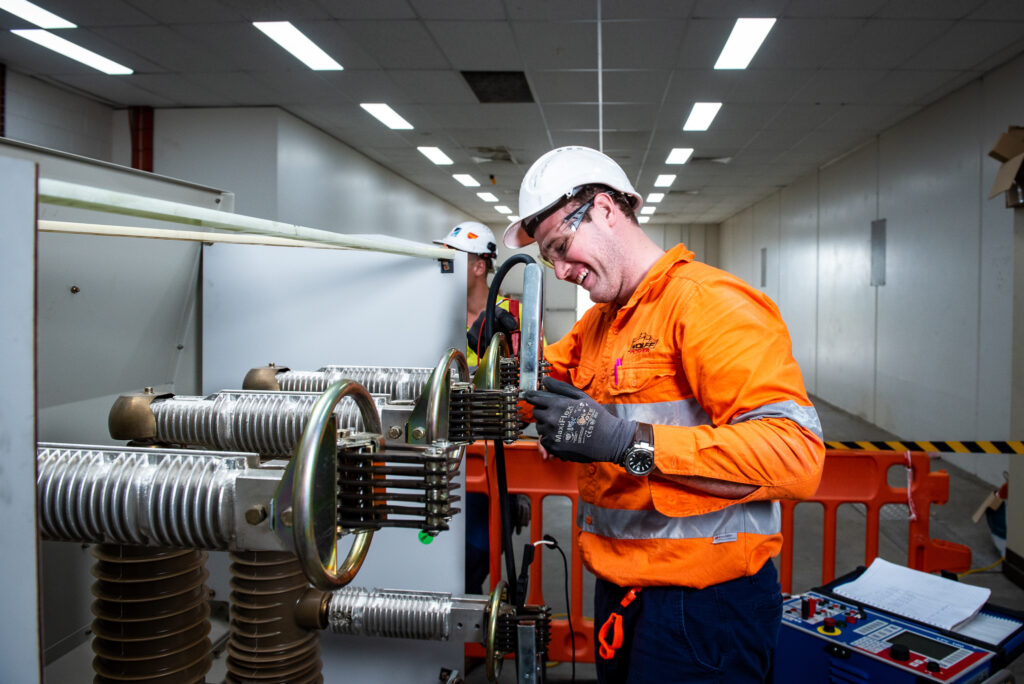

5. نکات ایمنی و نگهداری
با توجه به ولتاژ بالای کارکرد تابلوهای برق فشار قوی، رعایت نکات ایمنی و نگهداری بسیار حائز اهمیت است. این نکات شامل موارد زیر است:
بازرسیهای دورهای:
- بازرسی و نگهداری منظم تجهیزات فشار قوی یکی از الزامات اساسی برای جلوگیری از بروز حوادث است. بازرسی شامل بررسی شرایط عایق، اتصالات الکتریکی، و عملکرد مدار شکنها میشود. این بازرسیها باید به صورت ماهانه، فصلی و سالانه انجام شوند تا از عملکرد صحیح و ایمن تجهیزات اطمینان حاصل شود.
آموزش اپراتورها:
- اپراتورهای تابلوهای برق باید آموزشهای لازم را درباره نحوه کار با تجهیزات و خطرات مربوط به کار با ولتاژهای بالا دریافت کنند. این آموزشها شامل شناسایی و ارزیابی خطرات، تکنیکهای ایمنی، و روشهای صحیح واکنش به شرایط اضطراری است.
استفاده از تجهیزات حفاظتی:
- هنگام کار با تابلوهای برق فشار قوی، استفاده از تجهیزات ایمنی شخصی (PPE) مانند دستکشهای عایق، کفشهای ایمنی و عینکهای محافظ ضروری است. این تجهیزات به اپراتورها کمک میکند تا در برابر خطرات الکتریکی و مکانیکی محافظت شوند.
مستندسازی و ثبت اطلاعات:
- ثبت دقیق اطلاعات مربوط به نگهداری، بازرسی و تعمیرات انجام شده بر روی تجهیزات فشار قوی، به شناسایی الگوهای خرابی و پیشبینی نیازهای نگهداری در آینده کمک میکند. این مستندسازی باید شامل تاریخ، نوع بازرسی، وضعیت تجهیزات و هر گونه اقدام اصلاحی باشد.
پیشگیری از خطرات محیطی:
- تابلوهای برق باید در مکانهایی نصب شوند که از شرایط محیطی نامناسب مانند رطوبت زیاد، گرد و غبار و دماهای بالا محافظت شوند. همچنین، نصب سیستمهای تهویه مناسب برای جلوگیری از افزایش دما در داخل تابلوها بسیار مهم است.
نظارت و کنترل از راه دور:
- استفاده از سیستمهای نظارت و کنترل از راه دور میتواند به شناسایی مشکلات و خطاها در تابلوهای برق کمک کند. این سیستمها میتوانند اطلاعات مربوط به جریان، ولتاژ و وضعیت تجهیزات را به صورت لحظهای ارائه دهند و در صورت بروز مشکل، هشدارهای لازم را ارسال کنند.

نتیجهگیری
تابلوهای برق فشار قوی به عنوان یکی از اجزای کلیدی در سیستمهای توزیع برق، نیازمند طراحی و ساخت ویژهای هستند. شناخت انواع تابلوها و تجهیزات مرتبط با آنها میتواند به بهبود کارایی و ایمنی سیستمهای برق کمک کند. با توجه به پیشرفتهای تکنولوژیکی، استفاده از تابلوهای برق گازی (GIS) به عنوان یک گزینه مدرن و کارآمد در حال افزایش است.
Types of High Voltage Industrial Electrical Panels and Their Equipment Introduction
High voltage industrial electrical panels play a crucial role in controlling and distributing electrical energy as key components of electrical distribution systems. Due to the high operating voltage, these panels require special design and construction to ensure the safety and efficiency of the electrical system. In this article, we will examine the types of high voltage electrical panels, related equipment, applications, and safety considerations
Definition of High Voltage Electrical Panels
A high voltage electrical panel refers to metal enclosures that house electrical equipment for controlling, protecting, and distributing electricity. These panels are typically designed for voltages above 63 kV and are used in large industries, power stations, and distribution networks
Types of High Voltage Electrical Panels
High voltage electrical panels can be classified based on several criteria:
- By Structure:
- Metal Enclosed Panels: These panels have a metal enclosure that completely protects the internal equipment from environmental factors. They are generally suitable for common applications.
- Metal Clad Panels: These panels have separate compartments for switches, circuit breakers, and other equipment. This design provides greater safety and reduces the risks associated with short circuits.
- Compartment Type Panels: These panels consist of interconnected compartments designed to reduce costs and complexity while maintaining safety.
- Withdrawable Panels: This type of panel allows operators to easily withdraw equipment for maintenance. They are commonly used in large industrial settings.
- Gas-Insulated Switchgear (GIS): The use of SF6 gas as insulation in these panels enables compact and safe design. GIS is ideal for high voltage applications in limited spaces.
- By Voltage:
- Low Voltage Panels (LV): These panels are designed for voltages up to 1 kV and are primarily used in public electrical distribution applications.
- Medium Voltage Panels (MV): These panels are designed for voltages between 1 kV and 36 kV and are used in various industries, including petrochemicals and power generation.
- High Voltage Panels (HV): These panels operate at voltages above 36 kV and are typically used in power stations and large distribution networks.
Equipment in High Voltage Electrical Panels
Various equipment is found in high voltage electrical panels, each serving specific functions:
- Circuit Breakers:
- Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCB): These are used for protection against overload and short circuits in low voltage circuits.
- Automatic Circuit Breakers: Designed for protecting large loads in high voltage systems.
- Notable brands: Schneider Electric, Siemens, ABB.
- Transformers:
- Distribution Transformers: Used for voltage conversion in distribution systems.
- Power Transformers: Employed for high voltage energy transfer.
- Notable brands: General Electric (GE), Siemens, Mitsubishi Electric.
- Cables:
- High Voltage Cables: Used for transmitting electrical current in power stations and panels.
- Insulated Cables: Provide protection against electrical hazards.
- Notable brands: Nexans, Prysmian Group, Southwire.
- Fuses:
- Power Fuses: Protect equipment against overload and short circuits.
- Fast Fuses: Protect sensitive loads.
- Notable brands: Eaton, Littelfuse, Bussmann.
- Contactors:
- AC and DC Contactors: Used to control the turning on and off of motors and equipment.
- Notable brands: Siemens, Schneider Electric, Allen-Bradley.
- Protective Relays:
- Digital Protective Relays: Monitor electrical conditions and detect faults.
- Thermal Relays: Protect electric motors.
- Notable brands: SEL (Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories), ABB, GE.
Applications of High Voltage Electrical Panels
High voltage electrical panels are used in various industries, including:
- Electricity Distribution in Large Industries:
- These panels distribute electrical energy to heavy equipment and machinery in industries such as petrochemicals, steel, and mining. For instance, in large steel manufacturing plants like Tata Steel in India, high voltage panels are used to manage and distribute electricity to production and processing machines.
- Control and Protection of Electric Motors:
- High voltage panels control and protect electric motors in industrial processes such as pumps and compressors. For example, in offshore oil platforms, high voltage electrical panels are essential for supplying power to pump motors and other equipment.
- Power Stations and Distribution Networks:
- These panels are used in power stations to manage and distribute electrical energy to various regions. For example, the Hoover Dam power station in the United States uses high voltage panels to control the distribution of energy generated by the dam.
- Renewable Energy Systems:
- In solar and wind energy projects, high voltage electrical panels are critical for managing and distributing produced energy. For instance, in solar parks like Solar Star in California, high voltage panels are used for connecting to the national grid and controlling the flow of electricity.
- Underground Facilities:
- In mines and underground facilities, high voltage panels supply power and control equipment. For example, in the Grasberg mine in Indonesia, high voltage electrical panels are used to power heavy equipment and ventilation systems.
Safety and Maintenance Considerations
Due to the high operating voltage of high voltage electrical panels, adhering to safety and maintenance practices is crucial. Key points include:
- Regular Inspections:
- Conducting regular inspections and maintenance of high voltage equipment is essential to prevent accidents. Inspections should include checking insulation conditions, electrical connections, and circuit breaker functionality. These inspections should be performed monthly, quarterly, and annually to ensure safe and efficient operation.
- Operator Training:
- Operators of electrical panels should receive necessary training on how to operate the equipment and the associated hazards of working with high voltages. Training should include hazard identification and assessment, safety techniques, and proper responses to emergencies.
- Use of Protective Equipment:
- When working with high voltage electrical panels, the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as insulated gloves, safety shoes, and protective eyewear is essential. This equipment helps protect operators from electrical and mechanical hazards.
- Documentation and Record Keeping:
- Keeping detailed records of maintenance, inspections, and repairs on high voltage equipment helps identify failure patterns and anticipate future maintenance needs. Documentation should include dates, inspection types, equipment status, and any corrective actions taken.
- Environmental Hazard Prevention:
- Electrical panels should be installed in locations that protect them from unfavorable environmental conditions such as high humidity, dust, and extreme temperatures. Additionally, proper ventilation systems should be installed to prevent overheating inside the panels.
- Remote Monitoring and Control:
- Utilizing remote monitoring and control systems can help identify issues and faults in electrical panels. These systems can provide real-time information on current, voltage, and equipment status and send alerts in case of problems.
Conclusion
High voltage electrical panels, as key components of electrical distribution systems, require specialized design and construction. Understanding the types of panels and their related equipment can enhance the efficiency and safety of electrical systems. With ongoing technological advancements, the use of Gas-Insulated Switchgear (GIS) is increasingly becoming a modern and efficient option.
References
1. Hughes, A. (2015). *Electrical and Electronic Technology*. Pearson Education.
2. Mohan, N., Undeland, T. M., & Robbins, W. P. (2003). *Power Electronics: Converters, Applications, and Design*. Wiley.
3. Bollen, M. H. J., & Hassan, F. (2011). *Integration of Distributed Generation in the Power System*. Wiley.
4. CIGRÉ Technical Brochures and Working Group Reports on switchgear and substations.





