سیستمهای حفاظت در برابر صاعقه در برجها و ساختمانهای بلند مرتبه
Lightning Protection Systems for High-Rise Buildings
*تمام حقوق این مقاله برای سازه گستر پایتخت محفوظ است
کلمات کلیدی
سیستمهای حفاظت در برابر صاعقه، ساختمانهای بلند، تجهیزات الکتریکی، ایمنی، زمینگذاری، ترمینالهای هوایی، بررسی و نگهداری
مقدمه
ضربههای صاعقه یکی از خطرات طبیعی قابل توجهی هستند که میتوانند آسیبهای جدی به ساختمانهای بلند، به ویژه برجها، وارد کنند. با افزایش ارتفاع ساختمانها و توسعه زیرساختهای شهری، اهمیت حفاظت از این سازهها در برابر صاعقه به شدت افزایش یافته است. صاعقه میتواند منجر به خسارات مالی و جانی قابل توجهی شود و عدم وجود یک سیستم حفاظتی مؤثر میتواند پیامدهای جدی به دنبال داشته باشد.
شما می توانید برای خرید و اطلاع از قیمت انواع تجهیزات سیستمهای حفاظت در برابر صاعقه در برجها و ساختمانهای بلند مرتبه مورد نیاز خود از طریق مشاوره با کارشناسان سازه گستر پایتخت اقدام نمایید.
گروه سازه گستر پایتخت با تکیه بر بیش از 20 سال تجربه و فعالیت به عنوان تامین کننده تجهیزات و ملزومات صنعت برق کشور ( الکتریکال - مکانیکال - ابزار دقیق ) با افتخار آماده خدمت رسانی به فعالان صنعت برق و صاحبان صنایع می باشد.
شماره تماس : 32 20 17 66 - 021
پست الکترونیک: info@sazehgostarsgp.com
نشانی: تهران، میدان فردوسی، کوچه گلپرور، پلاک 20، واحد 25
اهمیت حفاظت در برابر صاعقه
ساختمانها بهخصوص در مناطق با فعالیت بالای صاعقه، مانند نواحی گرمسیری و مناطق کوهستانی، بیشتر در معرض خطر قرار دارند. مطالعات نشان میدهند که ساختمانهای بلند به دلیل ارتفاع و موقعیت خود، بیشتر از سایر ساختمانها در معرض صاعقه قرار میگیرند. آمارها نشان میدهند که در برخی مناطق، تعداد برخوردهای صاعقه با ساختمانها به طور قابل توجهی افزایش یافته است. به عنوان مثال، در ایالات متحده، سالانه هزاران بار صاعقه به ساختمانها برخورد میکند که میتواند منجر به آتشسوزی، آسیبهای ساختاری و خسارات مالی شود.
پیامدهای عدم وجود سیستم حفاظت
عدم وجود یک سیستم حفاظت مؤثر در برابر صاعقه میتواند به آسیبهای جدی منجر شود. این آسیبها میتوانند شامل موارد زیر باشند:
- آسیب به ساختار: صاعقه میتواند باعث تخریب سقف و دیوارها، و همچنین آسیب به عناصر سازهای مانند تیرکها و ستونها شود.
- خسارت به تجهیزات الکتریکی: نوسانات ولتاژ ناشی از صاعقه میتواند به تجهیزات الکتریکی، از جمله سیستمهای کامپیوتری و شبکههای برق آسیب بزند. این موضوع میتواند منجر به از دست رفتن دادهها و هزینههای تعمیر و جایگزینی بالا شود.
- خطرات جانی: صاعقه میتواند به شدت خطرناک باشد و به خصوص برای افرادی که در نزدیکی ساختمان هستند، میتواند آسیبهای جدی یا حتی مرگ به دنبال داشته باشد. به عنوان مثال، بر اساس آمار، هر ساله حدود 20 تا 30 نفر در ایالات متحده به دلیل برخورد صاعقه جان خود را از دست میدهند.
برقگیر 10 کیلوولت BWKG برای سیستم قطع کننده مدار برق فشار متوسط و بالا
اهداف سیستمهای حفاظت در برابر صاعقه
سیستمهای حفاظت در برابر صاعقه طراحی شدهاند تا از آسیبهای ناشی از صاعقه جلوگیری کنند. این سیستمها شامل چندین جزء و فناوری هستند که به طور یکپارچه عمل میکنند تا ایمنی ساختمان و ساکنان آن را تضمین کنند. هدف اصلی این سیستمها عبارتند از:
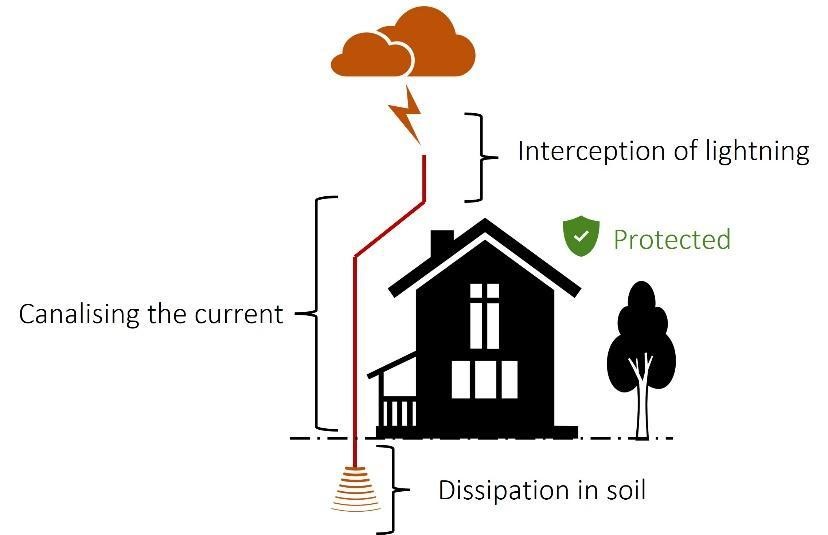
- تخلیه ایمن انرژی صاعقه: فراهم کردن یک مسیر ایمن برای جریان صاعقه به زمین، به طوری که از آسیب به ساختار و تجهیزات جلوگیری شود.
- محافظت از تجهیزات الکتریکی: استفاده از دستگاههای حفاظت از نوسانات (SPDs) برای جلوگیری از آسیب به تجهیزات الکتریکی.
- افزایش ایمنی ساکنان: ایجاد یک محیط ایمن برای ساکنان و کارکنان ساختمانها در برابر خطرات ناشی از صاعقه.
با توجه به این نکات، این مقاله به بررسی دقیقتر اصول، اجزا و بهترین شیوههای پیادهسازی سیستمهای حفاظت در برابر صاعقه در ساختمانهای بلند میپردازد و به تحلیل چالشها و راهکارهای موجود در این حوزه میپردازد.
درک صاعقه و اثرات آن
تعریف صاعقه
صاعقه یک تخلیه الکتریکی طبیعی است که در نتیجه تجمع بارهای الکتریکی در ابرها و زمین ایجاد میشود. این بارها به طور ناگهانی تخلیه میشوند و منجر به تولید جرقهای با ولتاژ بسیار بالا میگردند.
اثرات صاعقه
- آسیبهای فیزیکی: صاعقه میتواند منجر به آسیب به سقف، دیوارها و حتی سازههای داخلی ساختمان شود. به عنوان مثال، در سال 2019، یک ساختمان بلند در نیویورک به دلیل برخورد صاعقه با سقف، دچار آتشسوزی شد.
- فراوانی الکتریکی: نوسانات ولتاژ ناشی از صاعقه میتواند به تجهیزات الکتریکی آسیب بزند. برای مثال، صاعقه میتواند به سیستمهای کامپیوتری و شبکههای برق آسیب برساند و منجر به خرابی آنها شود.
- خطرات انسانی: آسیبهای جسمی ناشی از صاعقه میتواند برای افرادی که در نزدیکی ساختمان هستند، جدی باشد. بر اساس آمار، سالانه تعدادی از افراد در اثر صاعقه جان خود را از دست میدهند.
ارستر کلاس B+C هفت پل 350 ولت 100 کیلوآمپر سه فاز - مجهز به کنتاکت اعلام وضعیت - فونیکس کنتاکت
اصول حفاظت در برابر صاعقه
هدف سیستمهای حفاظت
هدف اصلی سیستمهای حفاظت در برابر صاعقه این است که یک مسیر ایمن برای جریانهای صاعقه فراهم کنند تا از آسیب به ساختمان و ساکنان جلوگیری شود.
روشهای حفاظتی
- انتشار زودهنگام جرقه (ESE): این فناوری به دور کردن صاعقه از ساختمان کمک میکند. سیستمهای ESE میتوانند با ایجاد یک جرقه زودهنگام، صاعقه را به سمت خود جذب کنند و از برخورد آن با ساختمان جلوگیری کنند.
سیستمهای زمینگذاری: این سیستمها با استفاده از میلههای زمین یا صفحات، انرژی صاعقه را به زمین منتقل میکنند. به عنوان مثال، در ساختمانهای بلند، معمولاً از چندین میله زمینگذاری استفاده میشود تا از انتقال انرژی صاعقه به داخل ساختمان جلوگیری شود.
- دستگاههای حفاظت از نوسانات (SPDs): این دستگاهها برای محافظت از تجهیزات الکتریکی در برابر نوسانات ولتاژ طراحی شدهاند. برای مثال، در بسیاری از ساختمانها از SPDs برای حفاظت از سرورهای کامپیوتری و تجهیزات حساس استفاده میشود.
برقگیر پلیمری فشار متوسط ۲۰kv تدبیر مولد تابان (TMT)
اجزای سیستمهای حفاظت در برابر صاعقه
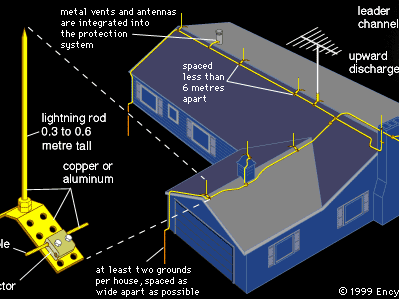
ترمینالهای هوایی
ترمینالهای هوایی نقاطی هستند که صاعقه به آنها برخورد میکند. این ترمینالها معمولاً در بالاترین نقاط ساختمان نصب میشوند و از جنس فلزات با هدایت الکتریکی بالا ساخته میشوند.
رساناها
رساناها مسیرهایی هستند که جریان صاعقه را از ترمینالها به سیستم زمینگذاری منتقل میکنند. این رساناها باید از موادی با مقاومت پایین ساخته شوند تا جریان به راحتی از آنها عبور کند.
سیستم زمینگذاری
سیستم زمینگذاری شامل میلهها، صفحات و مشهای زمین است که انرژی صاعقه را به زمین منتقل میکنند. طراحی صحیح این سیستمها برای اطمینان از ایمنی بسیار مهم است.
باندینگ
باندینگ به معنی اتصال تمام اجزای فلزی ساختمان به سیستم زمینگذاری است. این کار به جلوگیری از پدیدههای جانبی و خطرات ایمنی کمک میکند.
ارت سنج دیجیتال مدل UT572 ساخت کمپانیUNI-T
اجرای سیستم حفاظت در برابر صاعقه
مراحل اجرای سیستم
طراحی اولیه
- تحلیل ریسک: تحلیل نیازمندیها و خطرات موجود در محل ساختمان باید انجام شود. مثلاً، در مناطقی با فعالیت بالای صاعقه، نیاز به سیستمهای قویتری است.
- انتخاب تجهیزات: انتخاب تجهیزات مناسب بر اساس طراحی و استانداردها انجام میشود. برندهای معتبر مانند *OBO Bettermann* و *Erico* در این زمینه فعالیت دارند.
نصب ترمینالهای هوایی
ترمینالهای هوایی باید در بالاترین نقاط ساختمان نصب شوند. نصب آنها باید به گونهای باشد که به راحتی بتوانند صاعقه را جذب کنند. به عنوان مثال، استفاده از ترمینالهای ESE میتواند موثر باشد.
نصب رساناها
رساناها باید به گونهای نصب شوند که کمترین مقاومت را داشته باشند. استفاده از مواد با کیفیت و مقاوم در برابر زنگزدگی، مانند مس و آلومینیوم، توصیه میشود. برندهای معروف شامل *3M* و *nVent* هستند.
سیستم زمینگذاری
سیستمهای زمینگذاری باید به صورت عمق مناسب در زمین قرار گیرند. از میلههای استیل گالوانیزه برای افزایش عمر و کارایی سیستم استفاده میشود. برندهایی مانند *A. D. D.* و *ABB* در این زمینه شناخته شدهاند.
تست و ارزیابی
پس از نصب، تستهای عملکردی باید انجام شود تا اطمینان حاصل شود که سیستم به درستی کار میکند. این تستها شامل ارزیابی مقاومت زمین و بررسی اتصالات است.
تجهیزات و برندهای مهم
- ترمینالهای هوایی:
- OBO Bettermann
- Erico
- رساناها:
- 3M
- nVent
- سیستمهای زمینگذاری:
- A. D. D.
- ABB
- دستگاههای حفاظت از نوسانات (SPDs):
- Schneider Electric
- Siemens
ملاحظات طراحی
ارتفاع و ساختار ساختمان
ساختمانهای بلندتر به سیستمهای حفاظت بیشتری نیاز دارند. به عنوان مثال، در ساختمانهای بالاتر از 50 متر، چندین ترمینال هوایی و سیستمهای زمینگذاری بیشتری ضروری است.
موقعیت جغرافیایی
مناطق با فعالیت بالا در صاعقه، مانند نواحی گرمسیری، نیاز به سیستمهای قویتری دارند. به عنوان مثال، در جنوب ایالات متحده، ساختمانها باید با سیستمهای پیشرفتهتری طراحی شوند.
انطباق با استانداردها
رعایت استانداردهای ملی و بینالمللی، مانند NFPA 780 و IEC 62305، برای اطمینان از اثربخشی و ایمنی سیستم ضروری است.

نگهداری و بازرسی
بازرسیهای بصری
بازرسیهای منظم برای بررسی آسیبهای فیزیکی یا زنگزدگی اجزا باید انجام شود. این بازرسیها میتواند شامل بررسی ترمینالهای هوایی، رساناها و سیستم زمینگذاری باشد.
آزمون مقاومت زمین
آزمون مقاومت زمین برای اطمینان از اینکه سیستم زمینگذاری مقاومت پایینی را حفظ میکند تا انرژی صاعقه را به طور مؤثر تخلیه کند، ضروری است.
مستندسازی
نگهداری سوابق دقیق از بازرسیها و فعالیتهای نگهداری برای اطمینان از انطباق با مقررات ایمنی بسیار مهم است.
نتیجهگیری
پیادهسازی یک سیستم حفاظت مؤثر در برابر صاعقه در ساختمانهای بلند برای حفاظت از سازهها، سیستمهای الکتریکی و ساکنان در برابر خطرات صاعقه ضروری است. با درک اصول حفاظت در برابر صاعقه، استفاده از اجزای مناسب و رعایت استانداردهای طراحی، مالکان و مدیران ساختمان میتوانند به طور قابل توجهی خطرات ناشی از صاعقه را کاهش دهند. نگهداری و بازرسی منظم به افزایش قابلیت اطمینان این سیستمها کمک میکند و ایمنی و انطباق طولانیمدت را تضمین میکند.
Lightning Protection Systems for High-Rise Buildings
Keywords
Lightning protection systems
High-rise buildings
Electrical equipment
Safety
Grounding
Air terminals
Inspection and maintenance
Introduction
Lightning strikes are one of the significant natural hazards that can cause severe damage to tall buildings, particularly skyscrapers. With the increasing height of buildings and the development of urban infrastructure, the importance of protecting these structures from lightning has grown immensely. Lightning can lead to substantial financial and human losses, and the absence of an effective protective system can have serious consequences.
Importance of Lightning Protection
Buildings, especially in areas with high lightning activity, such as tropical and mountainous regions, are more vulnerable. Studies indicate that tall buildings are more frequently struck by lightning than other structures. Statistics show that in certain regions, the number of lightning strikes on buildings has significantly increased. For instance, in the United States, thousands of lightning strikes hit buildings annually, potentially resulting in fires, structural damage, and financial loss.
Consequences of Lacking Protection Systems
The absence of an effective lightning protection system can lead to serious damages, including:
- Structural Damage: Lightning can cause destruction to roofs and walls, as well as damage to structural elements such as beams and columns.
- Damage to Electrical Equipment: Voltage surges caused by lightning can harm electrical equipment, including computer systems and power networks. This can lead to data loss and high repair or replacement costs.
- Human Risks: Lightning can be extremely dangerous, and particularly for individuals near the building, it can cause severe injuries or even fatalities. For example, statistics reveal that around 20 to 30 people die in the United States each year due to lightning strikes.
Goals of Lightning Protection Systems
Lightning protection systems are designed to prevent damage caused by lightning strikes. These systems include various components and technologies that work together to ensure the safety of the building and its occupants. The primary objectives of these systems include:
- Safe Discharge of Lightning Energy: Providing a safe path for lightning current to the ground to prevent damage to the structure and equipment.
- Protection of Electrical Equipment: Utilizing surge protective devices (SPDs) to prevent damage to electrical equipment.
- Enhancing Occupant Safety: Creating a safe environment for occupants and staff in buildings against lightning hazards.
Given these points, this article will explore the principles, components, and best practices for implementing lightning protection systems in high-rise buildings and analyze the challenges and solutions within this field.
Understanding Lightning and Its Effects
Definition of Lightning
Lightning is a natural electrical discharge that occurs as a result of the accumulation of electrical charges in clouds and the ground. These charges are released suddenly, resulting in a spark with extremely high voltage.
Effects of Lightning
- Physical Damage: Lightning can cause damage to roofs, walls, and even the interiors of buildings. For instance, in 2019, a high-rise building in New York experienced a fire due to a lightning strike on its roof.
- Electrical Surges: Voltage fluctuations caused by lightning can damage electrical equipment. For example, lightning can harm computer systems and power networks, leading to failures.
- Human Risks: Physical injuries from lightning can be serious for individuals near the building. According to statistics, many people lose their lives due to lightning every year.
Principles of Lightning Protection
Purpose of Protection Systems
The primary purpose of lightning protection systems is to provide a safe pathway for lightning currents to prevent damage to the building and its occupants.
Protective Methods
- Early Streamer Emission (ESE): This technology helps divert lightning away from the building. ESE systems can attract lightning by creating an early discharge, preventing a direct strike.
- Grounding Systems: These systems use ground rods or plates to transfer lightning energy to the ground. For instance, in tall buildings, multiple grounding rods are typically used to prevent the transfer of lightning energy into the building.
- Surge Protective Devices (SPDs): These devices are designed to protect electrical equipment from voltage surges. Many buildings use SPDs to protect sensitive equipment such as computer servers.
Components of Lightning Protection Systems
Air Terminals
Air terminals are the points where lightning strikes. These terminals are typically installed at the highest points of the building and are made of highly conductive metals.
Conductors
Conductors are pathways that carry the lightning current from the air terminals to the grounding system. These conductors should be made of materials with low resistance to allow for easy current flow.
Grounding System
The grounding system consists of rods, plates, and grounding meshes that transfer lightning energy to the ground. Proper design of these systems is crucial for ensuring safety.
Bonding
Bonding refers to connecting all metallic components of the building to the grounding system. This helps prevent side effects and safety hazards.
Implementation of Lightning Protection Systems
Stages of Implementation
Initial Design
- Risk Analysis: Analyzing the requirements and hazards present at the building site must be conducted. For example, areas with high lightning activity require stronger systems.
- Equipment Selection: Choosing appropriate equipment based on design and standards is essential. Reputable brands like *OBO Bettermann* and *Erico* operate in this field.
Installing Air Terminals
Air terminals should be installed at the highest points of the building. Their installation must ensure that they can effectively attract lightning. For example, using ESE terminals can be effective.
Installing Conductors
Conductors should be installed to minimize resistance. It is recommended to use high-quality materials resistant to corrosion, such as copper and aluminum. Well-known brands include *3M* and *nVent*.
Grounding System
Grounding systems should be properly buried in the ground. Galvanized steel rods are used to enhance the durability and efficiency of the system. Brands like *A. D. D.* and *ABB* are recognized in this area.
Testing and Evaluation
After installation, performance tests must be conducted to ensure the system functions correctly. These tests include evaluating ground resistance and checking connections.
Key Equipment and Brands
- Air Terminals:
- OBO Bettermann
- Erico
- Conductors:
- 3M
- nVent
- Grounding Systems:
- A. D. D.
- ABB
- Surge Protective Devices (SPDs):
- Schneider Electric
- Siemens
Design Considerations
Height and Structure of the Building
Taller buildings require more extensive protection systems. For example, buildings taller than 50 meters typically necessitate multiple air terminals and additional grounding systems.
Geographic Location
Areas with high lightning activity, such as tropical regions, require more robust systems. For instance, buildings in the southern United States need advanced protection systems.
Compliance with Standards
Adhering to national and international standards, such as NFPA 780 and IEC 62305, is essential for ensuring the effectiveness and safety of the system.
Maintenance and Inspection
Visual Inspections
Regular inspections should be conducted to check for physical damage or corrosion of components. These inspections may include reviewing air terminals, conductors, and grounding systems.
Ground Resistance Testing
Testing ground resistance is crucial to ensure that the grounding system maintains low resistance for effectively discharging lightning energy.
Documentation
Maintaining accurate records of inspections and maintenance activities is vital for ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
Conclusion
Implementing an effective lightning protection system in high-rise buildings is essential for safeguarding structures, electrical systems, and occupants against lightning hazards. By understanding the principles of lightning protection, utilizing appropriate components, and adhering to design standards, building owners and managers can significantly reduce the risks associated with lightning strikes. Regular maintenance and inspections contribute to the reliability of these systems, ensuring long-term safety and compliance.
References
1. National Fire Protection Association. (2019). *NFPA 780: Standard for the Installation of Lightning Protection Systems*. NFPA.
2. International Electrotechnical Commission. (2010). *IEC 62305: Protection Against Lightning*. IEC.
3. CIGRÉ. (2018). *Benchmarking of Lightning Protection Systems for Transmission Lines*. CIGRÉ Technical Brochure.
4. R. G. & J. W. (2020). *High Voltage Transmission Systems Technology*. IET.
5. M. A. & S. N. (2020). *Designing High Voltage Transmission Lines*. Wiley.
6. T. H. B. & A. K. (2021). *High Voltage Engineering: Fundamentals and Applications*. Elsevier.
7. Johnson, E. (2018). *Electrical Power Systems Technology*. Pearson.
8. K. P. (2021). *Power System Stability and Control*. Wiley.
9. S. M. & N. R. (2018). *Fundamentals of Electric Power Transmission*. Springer.
10. B. R. & H. T. (2019). *Transmission Line Theory and Applications*. Springer.









