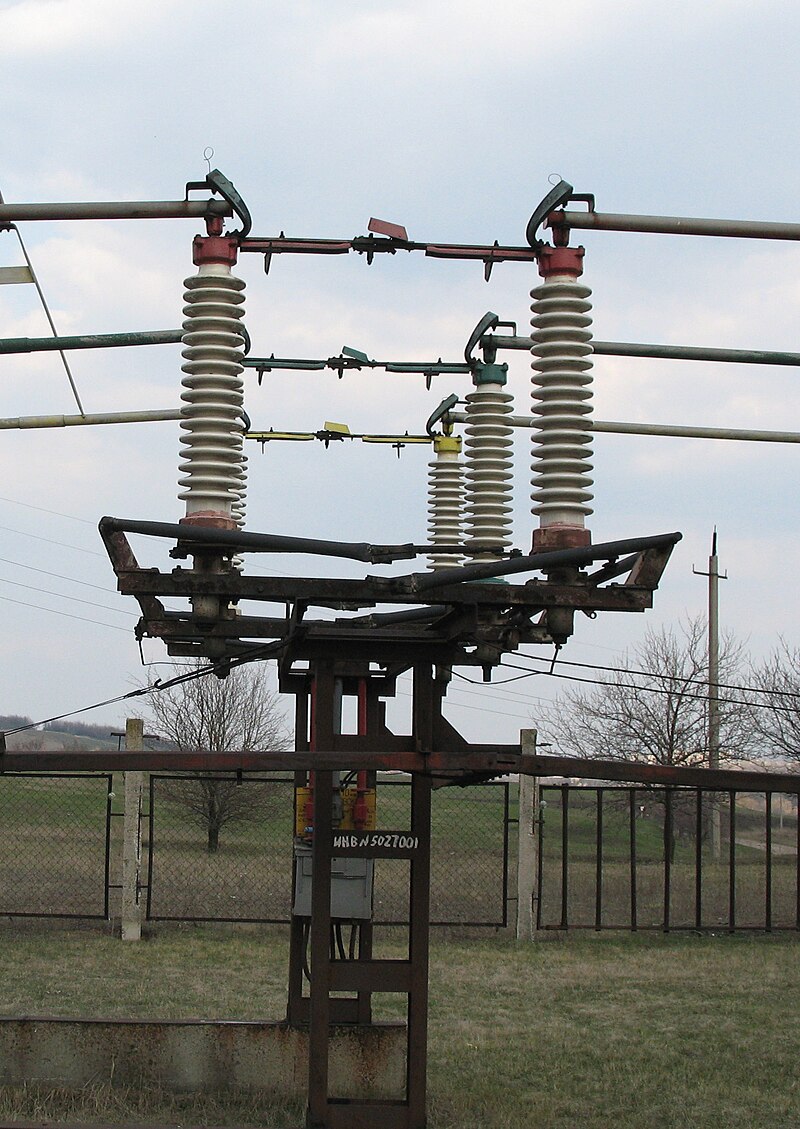
سکسیونرها در سیستمهای برق فشار قوی: کاربردها، عملکرد و اهمیت
*تمام حقوق این مقاله برای سازه گستر پایتخت محفوظ است
Disconnectors in High Voltage Power Systems: Applications, Functionality, and Importance
مقدمه
سکسیونرها (Disconnectors) ابزارهای حیاتی در سیستمهای توزیع و انتقال برق فشار قوی محسوب میشوند. این دستگاهها به منظور قطع و وصل جریان برق در شرایط مختلف طراحی شدهاند و در ایمنی و مدیریت شبکههای برق نقش کلیدی ایفا میکنند. با توجه به افزایش نیاز به انرژی و پیچیدگیهای شبکههای برق، درک دقیق عملکرد و کاربرد سکسیونرها برای مهندسان و تکنسینها ضروری است.
تعریف سکسیونر
سکسیونر یک نوع کلید است که برای قطع و وصل مدار به کار میرود. این دستگاهها به صورت مکانیکی یا الکتریکی عمل میکنند و طراحی آنها به گونهای است که در حالت قطع، هیچ جریانی از آنها عبور نکند. این ویژگی سکسیونرها را به ابزاری ایمن و قابل اعتماد برای استفاده در شبکههای برق فشار قوی تبدیل کرده است.
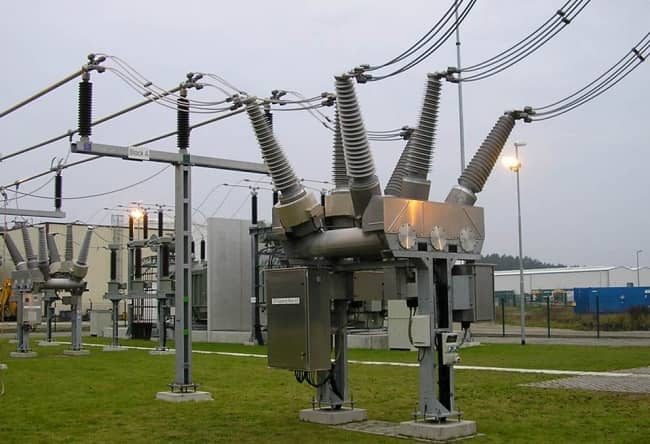

شما می توانید برای خرید و اطلاع از قیمت انواع سکسیونر ایرانی و خارجی مورد نیاز خود از طریق مشاوره با کارشناسان سازه گستر پایتخت اقدام نمایید.
گروه سازه گستر پایتخت با تکیه بر بیش از 20 سال تجربه و فعالیت به عنوان تامین کننده تجهیزات و ملزومات صنعت برق کشور ( الکتریکال - مکانیکال - ابزار دقیق ) با افتخار آماده خدمت رسانی به فعالان صنعت برق و صاحبان صنایع می باشد.
شماره تماس : 32 20 17 66 - 021
پست الکترونیک: info@sazehgostarsgp.com
نشانی: تهران، میدان فردوسی، کوچه گلپرور، پلاک 20، واحد 25
انواع سکسیونرها
سکسیونرهای مکانیکی
این نوع سکسیونرها معمولاً با استفاده از نیروی انسانی یا موتورها عمل میکنند. آنها به طور دستی یا با استفاده از سیستمهای هیدرولیکی و پنوماتیکی قابل کنترل هستند. سکسیونرهای مکانیکی به دلیل سادگی در طراحی و تعمیرات، در بسیاری از شبکههای برق مورد استفاده قرار میگیرند.
سکسیونرهای الکتریکی
این سکسیونرها به صورت خودکار و با استفاده از سیستمهای کنترلی عمل میکنند. آنها معمولاً شامل سنسورها و کنترلرهای الکترونیکی هستند که به واسطه آنها میتوان عملکرد سکسیونر را از راه دور کنترل کرد. سکسیونرهای الکتریکی به ویژه در سیستمهای پیچیده و بزرگ کاربرد دارند و به مدیران شبکه امکان میدهند که به راحتی شرایط شبکه را مدیریت کنند.
برای خرید سکسیونر ایران سوئیچ 24کیلوولت 630آمپر16کیلوآمپر کلیک کنید
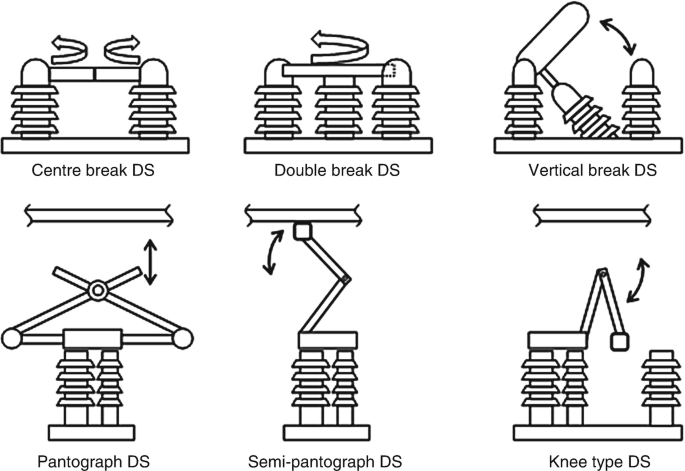
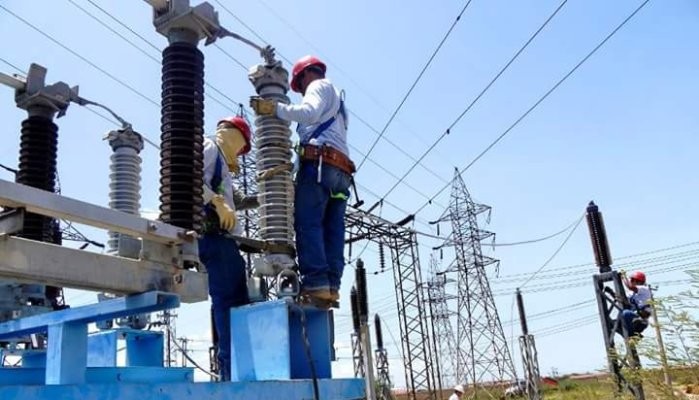
عملکرد سکسیونرها
عملکرد سکسیونرها در قطع و وصل برق به گونهای طراحی شده است که در زمان قطع، مدار را به طور کامل از شبکه جدا میکنند. این عمل به ایمنی کارکنان در هنگام تعمیر و نگهداری کمک میکند. سکسیونرها معمولاً در نقاط کلیدی شبکههای برق، مانند پستهای برق و ایستگاههای تبدیل، نصب میشوند.
مراحل عملکرد سکسیونر
1. تشخیص نیاز به قطع:
سیستمهای نظارتی به طور مداوم شرایط شبکه را بررسی میکنند و در صورت نیاز به قطع برق، سیگنالی به سکسیونر ارسال میشود.
2. قطع مدار:
سکسیونر با قطع جریان برق، مدار را از شبکه جدا میکند. این کار معمولاً با استفاده از مکانیزمهای مکانیکی یا الکتریکی انجام میشود.
3. تأیید قطع:
پس از قطع، سیستمهای نظارتی تأیید میکنند که سکسیونر به درستی عمل کرده و هیچ جریانی از آن عبور نمیکند.

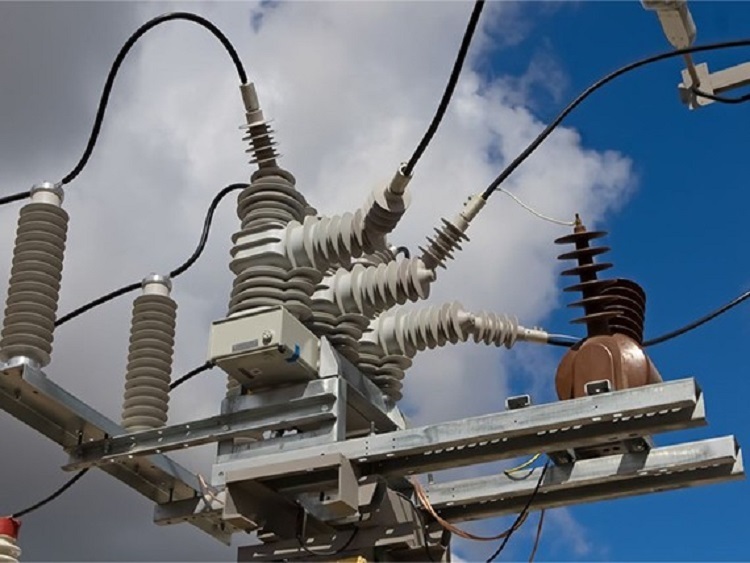
کاربردهای سکسیونر در برق فشار قوی
1. ایمنی
سکسیونرها به عنوان ابزاری برای ایمنی کارکنان در هنگام تعمیر و نگهداری عمل میکنند. با قطع کامل مدار، خطرات ناشی از برقگرفتگی به حداقل میرسد.
2. مدیریت بار
این تجهیزات به مدیران شبکه کمک میکنند تا بارهای مختلف را مدیریت کرده و از بروز مشکلاتی مانند اضافه بار جلوگیری نمایند. سکسیونرها به عنوان ابزارهایی برای تنظیم و توزیع بار در زمانهای اوج مصرف، بسیار مؤثر هستند.
3. فصلبندی و تعمیر
سکسیونرها امکان فصلبندی بخشهای مختلف شبکه را فراهم کرده و به تعمیر و نگهداری آسانتر کمک میکنند. این ویژگی به مهندسان اجازه میدهد تا بدون ایجاد اختلال در کل شبکه، به تعمیرات و نگهداری بخشهای خاص بپردازند.
برای خرید سوئیچ قطع برق 126kv تک قطبی عایق برق در فضای باز برند Tianan Electric کلیک کنید

چالشها و آینده سکسیونرها
با پیشرفت فناوری، سکسیونرها نیز در حال تحول هستند. چالشهایی مانند افزایش فشار بر روی شبکهها، نیاز به اتوماسیون و کاهش هزینهها، نیازمند توسعه و طراحی سکسیونرهای جدید با کارایی بالاتر است. همچنین، استفاده از تکنولوژیهای هوشمند در سکسیونرها میتواند به بهبود عملکرد و مدیریت بهتر شبکههای برق کمک کند.
نتیجهگیری
سکسیونرها به عنوان یکی از اجزای کلیدی در سیستمهای برق فشار قوی، نقش بسزایی در ایمنی و کارایی شبکههای برق ایفا میکنند. آموزش و آگاهی در مورد عملکرد و نصب آنها برای مهندسان و تکنسینها ضروری است. با توجه به پیشرفتهای تکنولوژیک و نیاز روزافزون به انرژی، اهمیت سکسیونرها در آینده بیشتر از قبل خواهد شد.
Disconnectors in High Voltage Power Systems: Applications, Functionality, and Importance
Introduction
Disconnectors are critical tools in high voltage power distribution and transmission systems. These devices are designed to switch electrical currents under various conditions and play a key role in the safety and management of power networks. Given the increasing demand for energy and the complexity of power systems, a thorough understanding of disconnectors' functionality and applications is essential for engineers and technicians
Definition of Disconnectors
A disconnector is a type of switch used to break and make circuits. These devices operate either mechanically or electrically, and their design ensures that no current flows through them when in the open position. This characteristic makes disconnectors safe and reliable tools for use in high voltage power networks
Types of Disconnectors
Mechanical Disconnectors
These disconnectors typically operate using human force or motors. They can be controlled manually or through hydraulic and pneumatic systems. Mechanical disconnectors are widely used in many power networks due to their simplicity in design and ease of maintenance
Electrical Disconnectors
These disconnectors operate automatically using control systems. They usually include sensors and electronic controllers that allow for remote operation. Electrical disconnectors, particularly in complex and large systems, provide network managers with the ability to easily manage network conditions
Functionality of Disconnectors
The functionality of disconnectors is designed to fully isolate a circuit from the network during power interruption. This action enhances worker safety during maintenance and repair operations. Disconnectors are typically installed at critical points in power networks, such as substations and conversion stations
Steps in Disconnector Operation
Detection of the Need to Disconnect
Monitoring systems continuously assess network conditions, and if disconnection is needed, a signal is sent to the disconnector
Circuit Break
The disconnector isolates the circuit from the power network. This process is usually performed through mechanical or electrical mechanisms
Confirmation of Disconnection
After disconnection, monitoring systems confirm that the disconnector has operated correctly and that no current is flowing through it
Applications of Disconnectors in High Voltage Power Systems
Safety
Disconnectors serve as a safety tool for workers during maintenance and repair. By completely isolating circuits, the risk of electric shock is minimized
Load Management
These devices assist network managers in managing various loads and preventing problems such as overloads. Disconnectors are particularly effective as tools for adjusting and distributing loads during peak consumption times
Segmentation and Repair
Disconnectors facilitate the segmentation of different sections of the network, aiding in easier maintenance and repair. This feature allows engineers to carry out repairs on specific sections without disrupting the entire network
Challenges and Future of Disconnectors
As technology advances, disconnectors are also evolving. Challenges such as increasing pressure on networks, the need for automation, and cost reduction necessitate the development and design of new disconnectors with higher efficiency. Additionally, the use of smart technologies in disconnectors can enhance performance and better management of power networks
Conclusion
Disconnectors play a crucial role as key components in high voltage power systems, significantly impacting the safety and efficiency of power networks. Education and awareness regarding their operation and installation are essential for engineers and technicians. With technological advancements and the growing demand for energy, the importance of disconnectors will continue to increase in the future.
منابع:
1. IEEE Std 100-2000. (2000). *IEEE Standard Dictionary of Electrical and Electronic Terms*.
2. B. H. Khan, "Electrical Power Systems," 4th ed. McGraw-Hill, 2011.
3. G. R. Slemon, "Electric Machines," 2nd ed. Wiley, 1999.
4. M. H. Rashid, "Power Electronics: Circuits, Devices & Applications," 4th ed. Pearson, 2014.