تجهیزات برق خطوط مترو
Electric Equipment of Metro Lines
*تمام حقوق این مقاله برای سازه گستر پایتخت محفوظ است
چکیده
با توجه به رشد سریع شهرنشینی و نیاز به حمل و نقل عمومی کارآمد، خطوط مترو به عنوان یکی از مؤثرترین شیوههای حمل و نقل شهری به شمار میروند. تجهیزات برق در این سیستمها از اهمیت بالایی برخوردارند و شامل اجزای مختلفی همچون تأسیسات برق، خطوط تغذیه و سیستمهای کنترل میشوند. این مقاله به بررسی تجهیزات برق خطوط مترو و اهمیت آنها در بهبود کارایی و ایمنی مترو میپردازد و چالشهای موجود در این حوزه را تحلیل میکند.
واژگان کلیدی
- تجهیزات برقی مترو
- تأسیسات برقی
- خطوط تغذیه
- سیستمهای کنترل
- ایمنی مترو
- مدیریت ترافیک
- ارتباطات بیسیم
- انرژی تجدیدپذیر
- تعمیر و نگهداری
شما می توانید برای خرید و اطلاع از قیمت تجهیزات برق خطوط مترو مورد نیاز خود از طریق مشاوره با کارشناسان سازه گستر پایتخت اقدام نمایید.
گروه سازه گستر پایتخت با تکیه بر بیش از 20 سال تجربه و فعالیت به عنوان تامین کننده تجهیزات و ملزومات صنعت برق کشور ( الکتریکال - مکانیکال - ابزار دقیق ) با افتخار آماده خدمت رسانی به فعالان صنعت برق و صاحبان صنایع می باشد.
شماره تماس : 32 20 17 66 - 021
پست الکترونیک: info@sazehgostarsgp.com
نشانی: تهران، میدان فردوسی، کوچه گلپرور، پلاک 20، واحد 25
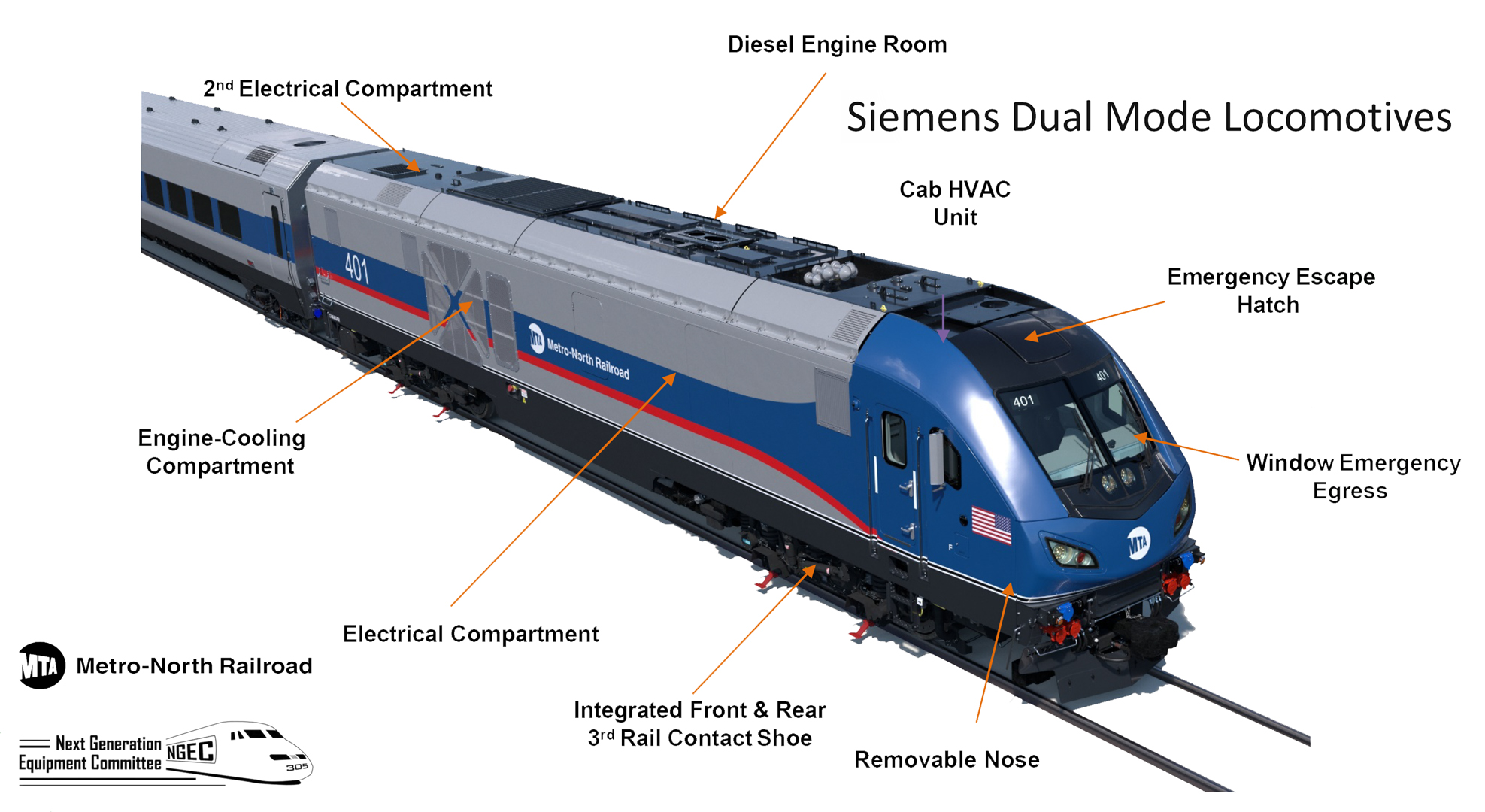
مقدمه
خطوط مترو به عنوان یکی از مهمترین وسایل حمل و نقل عمومی در شهرها، نقش کلیدی در کاهش ترافیک و آلودگی هوا دارند. تجهیزات برق، عنصر حیاتی در این سیستمها هستند که به تأمین انرژی و کنترل عملیات قطارها کمک میکنند. با افزایش تقاضا برای حمل و نقل عمومی و فشار بر روی شبکههای حمل و نقل، بهینهسازی و توسعه تجهیزات برقی در خطوط مترو از اهمیت بالایی برخوردار است.
1. اجزای اصلی سیستمهای برقی مترو
این بخش به بررسی اجزای اساسی سیستمهای برقی مترو پرداخته و نقش هر یک از آنها را تشریح میکند.
1.1 تأسیسات برق
تأسیسات برق شامل زیرساختهای حیاتی هستند که انرژی الکتریکی را به سیستمهای مترو تأمین میکنند.
ایستگاههای برق: مراکز تأمین انرژی که شامل تجهیزات زیر هستند:
- ترانسفورماتورها: مانند ترانسفورماتورهای شرکت Siemens و Schneider Electric که انرژی الکتریکی را به ولتاژهای مناسب تبدیل میکنند.
- تابلوهای تقسیم: تابلوهای قدیمی و جدید برندهایی مانند ABB و Eaton میتوانند برای توزیع برق مورد استفاده قرار گیرند.
میکرو شبکهها: یکی از نوآوریهای جدید در تأسیسات برقی است که میتواند به تأمین انرژی محلی و ترکیب آن با منابع تجدیدپذیر کمک کند.

1.2 خطوط تغذیه
این خطوط وظیفه تأمین انرژی الکتریکی به قطارها را بر عهده دارند و میتوانند به دو دسته تقسیم شوند:
خطوط هوایی (Overhead Lines): این خطوط به عنوان منبع اصلی تغذیه انرژی الکتریکی برای قطارها عمل میکنند.
- سیستمهای OCS (Overhead Contact Systems): محصولات برندهایی همچون Pandrol و Vossloh منجر به بهبود عملکرد و کاهش نویز در خطوط هوایی میشوند.
خطوط زیرزمینی (Underground Lines): این سیستمها به خصوص در مناطقی که فضا محدود است یا در نقاط حساس شهری قرار دارند.
- کابلهای مناسب: کابلهای برق از برندهای مختلف مانند Prysmian و Nexans برای این نوع سیستمها پیشنهاد میشوند.
1.3 سیستم کنترل
سیستمهای کنترل در خطوط مترو وظیفه نظارت، مدیریت و هماهنگی حرکت قطارها را بر عهده دارند.
سیستمهای مدیریت ترافیک: این سیستمها با استفاده از نرمافزارهای پیشرفته نظیر SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition) میتوانند به خدمات حمل و نقل کمک کنند. برندهایی مانند Indra و Thales در این زمینه فعالیت دارند.
سیستمهای ارتباطی: شامل ارتباطات رادیویی و بیسیم هستند که به کارمندان و مسئولان امکان میدهد تا در مواقع اضطراری به سرعت واکنش نشان دهند.
- تجهیزات ارتباطی: برندهایی مانند Motorola و Nokia در ارائه تجهیزات ارتباطی بیسیم فعال هستند.
فناوری راهبر خودکار (ATO): این فناوری به اتوماسیون حرکت قطارها کمک میکند و از طریق الگوریتمهای پیچیده، کنترل سرعت و توقف قطار را مدیریت مینماید. برندهای ارائهدهنده ATO شامل Bombardier و Alstom هستند.
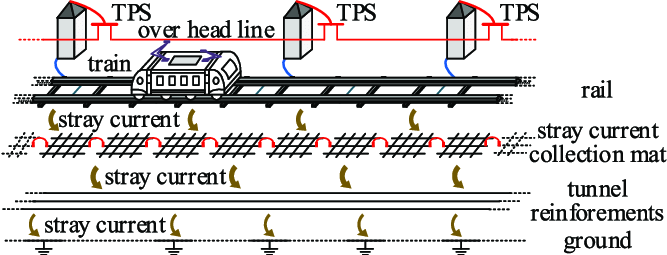
2. تأسیسات و تجهیزات تغذیه برق
تأسیسات و تجهیزات تغذیه برق بخشی جداییناپذیر از سیستمهای مترو هستند و به مرکز تأمین انرژی الکتریکی تبدیل میشوند.
2.1 تأسیسات قدرت
این تأسیسات شامل موارد زیر هستند:
ایستگاههای ترانسفورماتور: برای تبدیل ولتاژ در انرژی الکتریکی استفاده میشوند.
- ترانسفورماتورهای AC و DC: برندهایی مانند Toshiba و Siemens به تولید ترانسفورماتورهای مناسب در این مقیاس پرداخته و کاربردهای خاص مترو را در نظر میگیرند.
ژنراتورها و منابع انرژی:
- سیستمهای انرژی تجدیدپذیر: پنلهای خورشیدی از برندهایی مثل SunPower وCanadian Solar میتوانند به تأمین انرژی مترو کمک کنند.
2.2 رویههای بهرهبرداری
اقدامات انجام شده برای بهبود کارایی تأسیسات تغذیه شامل بهینهسازی فرآیندها و استفاده از فناوریهای نوین است.
بهرهبرداری بهینه از منابع: با استفاده از نرمافزارهای مدیریت انرژی (Energy Management Software) میتوان بر اساس بار مصرفی، تنظیمات خاصی را انجام داد.
نگهداری پیشگیرانه: اجرای برنامههای نگهداری منظم به حفظ عملکرد تجهیزات و جلوگیری از خرابیها کمک میکند.
- نرمافزارهای CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems): برندهایی مانند IBM Maximo و Infor CloudSuite برای انجام این کار مناسب هستند.

3. سیستمهای کنترل و ارتباط
سیستمهای کنترل و ارتباط در خطوط مترو از راههای مختلفی برای بهبود ایمنی و کارایی استفاده میکنند.
3.1 سیستمهای کنترل خودکار
این سیستمها به کنترل عملکرد قطارها، کاهش خطر برخورد و بهبود جابجایی مسافران کمک میکنند.
سیستم کنترل ترافیک: این سیستمها شامل ابزارهای نظارتی و مدیریت الگوریتمها برای حرکت سریع و ایمن قطارها هستند.
- نرمافزارهای مدیریت ترافیک: برندهای Siemens و Alstom در ارائه این گونه نرمافزارها بسیار پیشرفته هستند.
سیستمهای علامتگذاری: که وضعیت خطوط را اعلام میکند و به رانندگان اطلاعات لازم را میدهد.
- سیستمهای سیگنالینگ: از برندهایی مانند Thales و Bombardier میتوان در این باره نام برد.
3.2 ارتباطات اندرکنشی
این بخش شامل ارتباط میان قطارها، ایستگاهها و مرکز کنترل است.
تجهیزات ارتباطی داخلی: مانند تلفنهای اضطراری و سیستمهای ارتباطی بیسیم از برندهای معتبری همچون Hytera و Harris.
سیستمهای نظارت تصویری: با استفاده از دوربینهای مدار بسته مانند محصولات Hikvision و Dahua میتوان بر روی ایستگاهها و خطها نظارت کرد.

4. چالشها و راهکارها
این بخش به چالشهای موجود در تجهیزات و زیرساختهای برق خطوط مترو میپردازد و پیشنهادات لازم برای بهبود آنها را ارائه میدهد.
4.1 چالشها
خرابی و نگهداری: یکی از چالشهای اصلی، نیاز به نگهداری پیوسته و جلوگیری از خرابی تجهیزات است که میتواند منجر به اختلالات در خدمات شود.
تأمین منابع مالی: تأمین مالی برای بهروزرسانی و نگهداری تجهیزات برقی میتواند مشکلساز باشد.
4.2 راهکارها
استفاده از فناوریهای نوین: بهکارگیری فناوریهای پیشرفته و هوش مصنوعی در مدیریت و کنترل سیستم میتواند هزینههای عملیاتی را کاهش دهد.
برنامههای آموزشی و ارتقاء مهارتها: برگزاری دورههای آموزشی برای پرسنل در زمینه تکنولوژیهای جدید و نکات ایمنی برای حفظ بهرهوری بالا.
ایجاد همکاری بینالمللی: توسعه همکاری با شرکتهای جهانی برای انتقال فناوریهای نوین و به اشتراکگذاری تجربیات.

5. نتیجهگیری
بهینهسازی تجهیزات برقی خطوط مترو یکی از نیازهای اساسی برای ارائه خدمات حمل و نقل عمومی کارآمد و ایمن است. با توجه به رشد شهرنشینی و تقاضا برای حمل و نقل عمومی، نیاز به سرمایهگذاری در تکنولوژی و آموزش نیروی انسانی احساس میشود.
تحلیل چالشها و ارائه راهکارهای مؤثر در این مقاله میتواند به بهبود عملکرد سیستمهای مترو کمک کرده و به امنیت و راحتی مسافران افزوده شود.
منابع
- هوا، ج. (1399). "بررسی تجهیزات برق و ایستگاههای مترو". مجله مهندسی برق.
- موسوی، ر. (1400). "تحلیل عملکرد سیستمهای تغذیه برق در خطوط مترو". کنفرانس بینالمللی حمل و نقل شهری.
- اصغری، م. (1398). "سیستمهای کنترل و ارتباط در خطوط مترو". مجله فنآوریهای نوین حمل و نقل.
- غفاری، س. (1401). "مدیریت انرژی در خطوط مترو". نشریه تحقیقات حمل و نقل.
- کریمی، ف. (1397). "ایمنی در سیستمهای برقی مترو". سمینار ایمنی و حمل و نقل.
- مرادی، م. و رسولی، ل. (1400). "تحقیقات جدید در زمینه خطوط تغذیه و تجهیزات مترو". مجله علوم وابسته به حمل و نقل.
- رضا، ن. (1397). "استفاده از فناوریهای نوین در سیستمهای برقی مترو". پژوهشهای مهندسی برق.
- شریفی، ح. (1399). "نقش تأسیسات برقی در افزایش ایمنی مترو". مجله ایمنی و حفاظت از زیرساختها.
- سعادتی، ش. (1402). "مدیریت ریسک در تجهیزات برقی خطوط مترو". کنفرانس علمی حمل و نقل.
- نیکزاد، ی. (1401). "تحلیل کیفیت انرژی در سیستمهای مترو". مجله الکترونیک و سیستمهای قدرت.
Electric Equipment of Metro Lines
Abstract
Due to rapid urbanization and the need for efficient public transportation, metro lines have become one of the most effective means of urban transport. Electric equipment in these systems is of high importance, comprising various components such as power installations, feeding lines, and control systems. This paper examines the electric equipment of metro lines, its importance in improving efficiency and safety, and the challenges faced in this domain
Keywords
- Electric equipment metro
- Power installations
- Feeding lines
- Control systems
- Metro safety
- Traffic management
- Wireless communications
- Renewable energy
- Maintenance
Introduction
Metro lines, as one of the most important public transportation modes in cities, play a key role in reducing traffic congestion and air pollution. Electric equipment is a vital component of these systems that helps supply energy and control train operations. With the increasing demand for public transportation and pressure on transport networks, optimizing and developing electric equipment in metro lines is of utmost importance
1. Main Components of Electric Systems in Metro
This section discusses the essential components of electric systems in metro lines and describes the role of each.
1.1 Power Installations
Power installations include critical infrastructure that supplies electrical energy to the metro systems.
Power Stations: These energy supply centers include:
- Transformers: Such as transformers from companies like Siemens and Schneider Electric that convert electrical energy to suitable voltages.
- Distribution Panels: Old and new panels from brands like ABB and Eaton can be used for electricity distribution.
Microgrids: One of the new innovations in power installations that can help in local energy supply and the integration of renewable sources.
1.2 Feeding Lines
These lines are responsible for providing electrical energy to the trains and can be divided into two categories:
Overhead Lines: These lines serve as the main energy supply source for trains.
- OCS Systems (Overhead Contact Systems): Products from brands like Pandrol and Vossloh improve performance and reduce noise in overhead lines.
Underground Lines: These systems are particularly useful in areas with limited space or in sensitive urban spots.
- Suitable Cables: Power cables from various brands, such as Prysmian and Nexans, are recommended for these types of systems.
1.3 Control Systems
Control systems in metro lines are responsible for monitoring, managing, and coordinating train movements.
Traffic Management Systems: These systems can help in providing transport services with advanced software such as SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition). Companies like Indra and Thales are active in this area.
Communication Systems: These include radio and wireless communications that allow employees and officials to react quickly in emergencies.
- Wireless Communication Equipment: Brands like Motorola and Nokia are active in providing wireless communication devices.
Automatic Train Operation (ATO) Technology: This technology helps automate train movements, managing train speed and stops through complex algorithms. Brands offering ATO include Bombardier and Alstom.
2. Power Supply Installations and Equipment
Power supply installations and equipment are an essential part of metro systems and serve as energy supply centers.
2.1 Power Facilities
These facilities include:
Transformer Stations: Used for voltage conversion in electrical energy.
- AC and DC Transformers: Brands like Toshiba and Siemens produce suitable transformers for this scale while considering specific metro applications.
Generators and Energy Sources:
- Renewable Energy Systems: Solar panels from brands like SunPower and Canadian Solar can help supply energy to the metro.
2.2 Operational Procedures
Actions taken to improve the efficiency of power supply facilities include optimizing processes and utilizing new technologies.
Optimal Utilization of Resources: Using Energy Management Software can help adjust configurations based on consumption loads.
Preventive Maintenance: Implementing regular maintenance programs helps maintain equipment performance and prevent breakdowns.
- CMMS Software (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems): Brands like IBM Maximo and Infor CloudSuite are suitable for this purpose.
3. Control and Communication Systems
Control and communication systems in metro lines utilize various methods to improve safety and efficiency.
3.1 Automated Control Systems
These systems help control train performance, reduce collision risks, and enhance passenger flow.
Traffic Control Systems: These systems include supervisory tools and management algorithms for fast and safe train movement.
- Traffic Management Software: Brands like Siemens and Alstom are advanced in offering this type of software.
Signaling Systems: Indicating the status of lines and providing drivers with necessary information.
- Signaling Systems: Brands like Thales and Bombardier offer advanced systems in this regard.
3.2 Interoperable Communications
This section includes communication among trains, stations, and control centers.
Internal Communication Equipment: Such as emergency telephones and wireless communication systems from reputable brands like Hytera and Harris.
Video Surveillance Systems: Utilizing CCTV cameras from brands like Hikvision and Dahua can provide monitoring for stations and tracks.
4. Challenges and Solutions
This section discusses the challenges existing in electrical equipment and infrastructures of metro lines and suggests necessary improvements.
4.1 Challenges
Breakdowns and Maintenance: One of the main challenges is the need for continuous maintenance and prevention of equipment failures which can lead to service disruptions.
Financing: Securing funds for upgrading and maintaining electrical equipment can be challenging.
4.2 Solutions
Utilizing New Technologies: Employing advanced technologies and artificial intelligence in management and control systems can reduce operational costs.
Training and Skill Enhancement Programs: Holding training courses for staff on new technologies and safety tips helps maintain high efficiency.
International Collaboration: Developing partnerships with global companies for technology transfer and sharing experiences.
5. Conclusion
Optimizing electrical equipment in metro lines is one of the essential needs for providing efficient and safe public transportation services. With the growth of urbanization and demand for public transport, investment in technology and training of personnel is essential.
Analyzing challenges and providing effective solutions in this article can contribute to enhancing the performance of metro systems and improving the safety and comfort of passengers.
References
- Hava, J. (1399). "Review of Electric Equipment and Metro Stations." Journal of Electrical Engineering.
- Mousavi, R. (1400). "Performance Analysis of Electric Feeding Systems in Metro Lines." International Conference on Urban Transportation.
- Asgari, M. (1398). "Control and Communication Systems in Metro Lines." Journal of New Transportation Technologies.
- Ghafari, S. (1401). "Energy Management in Metro Lines." Research Journal of Transportation.
- Karimi, F. (1397). "Safety in Electric Systems for Metro." Seminar on Safety and Transport.
- Moradi, M. & Rasouli, L. (1400). "Recent Research in Feeding Lines and Equipment for Metro." Journal of Related Transportation Sciences.
- Reza, N. (1397). "Use of New Technologies in Electric Systems of Metro." Engineering Research Journal.
- Sharifi, H. (1399). "The Role of Electric Installations in Improving Metro Safety." Journal of Infrastructure Safety and Protection.
- Saadati, Sh. (1402). "Risk Management in Electric Equipment of Metro Lines." Scientific Conference on Transport.
- Nikzad, Y. (1401). "Quality Analysis of Energy in Metro Systems." Journal of Electronics and Power Systems.






