توربین گازی: قلب تپنده صنایع، نیروگاهها و نقش آن در برق صنعتی
Gas Turbine: The Beating Heart of Industries, Power Plants, and Its Role in Industrial Electricity
*تمام حقوق این مقاله برای سازه گستر پایتخت محفوظ است
واژگان کلیدی:
توربین گازی، نیروگاه گازی، تولید برق، کمپرسور، محفظه احتراق، راندمان توربین گازی، نگهداری توربین گازی، کاربردهای توربین گازی، انواع توربین گازی، برق صنعتی، سیستم CHP، تولید همزمان برق و حرارت، توربین گازی راندمان بالا، کاهش آلایندگی توربین گازی، توربین گازی سوخت جایگزین
چکیده:
توربینهای گازی به عنوان یکی از مهمترین مولدهای توان در صنایع مختلف، نقش کلیدی در تولید برق و تامین انرژی ایفا میکنند. این مقاله به بررسی جامع عملکرد، اجزا، کاربردها، مزایا و معایب توربینهای گازی میپردازد. همچنین، به بررسی روندهای نوین و آینده این فناوری، به ویژه در زمینه برق صنعتی و تولید همزمان برق و حرارت (CHP) پرداخته میشود. هدف از این مقاله، ارائه یک دیدگاه کامل و بهروز در مورد توربینهای گازی و نقش آنها در صنعت انرژی است.
شما می توانید برای خرید و اطلاع از قیمت تجهیزات برق صنعتی در نیروگاههای برق از طریق مشاوره با کارشناسان سازه گستر پایتخت اقدام نمایید.
گروه سازه گستر پایتخت با تکیه بر بیش از 20 سال تجربه و فعالیت به عنوان تامین کننده تجهیزات و ملزومات صنعت برق کشور ( الکتریکال - مکانیکال - ابزار دقیق ) با افتخار آماده خدمت رسانی به فعالان صنعت برق و صاحبان صنایع می باشد.
شماره تماس : 32 20 17 66 - 021
پست الکترونیک: info@sazehgostarsgp.com
نشانی: تهران، میدان فردوسی، کوچه گلپرور، پلاک 20، واحد 25
مقدمه:
در دنیای امروز، انرژی به عنوان یکی از اساسیترین نیازهای بشر، نقش حیاتی در توسعه اقتصادی و اجتماعی ایفا میکند. توربینهای گازی، به عنوان یکی از مهمترین منابع تولید انرژی، در صنایع مختلف از جمله نیروگاهها، صنایع نفت و گاز، و صنایع هوافضا کاربرد گستردهای دارند. این ماشینهای قدرتمند، با تبدیل انرژی حاصل از احتراق سوخت به انرژی مکانیکی، امکان تولید برق، حرکت دادن تجهیزات و تامین حرارت مورد نیاز صنایع را فراهم میکنند. توربینهای گازی به دلیل مزایایی همچون راندمان بالا، قابلیت اطمینان و انعطافپذیری در استفاده از سوختهای مختلف، به یک گزینه جذاب برای تولید انرژی تبدیل شدهاند.
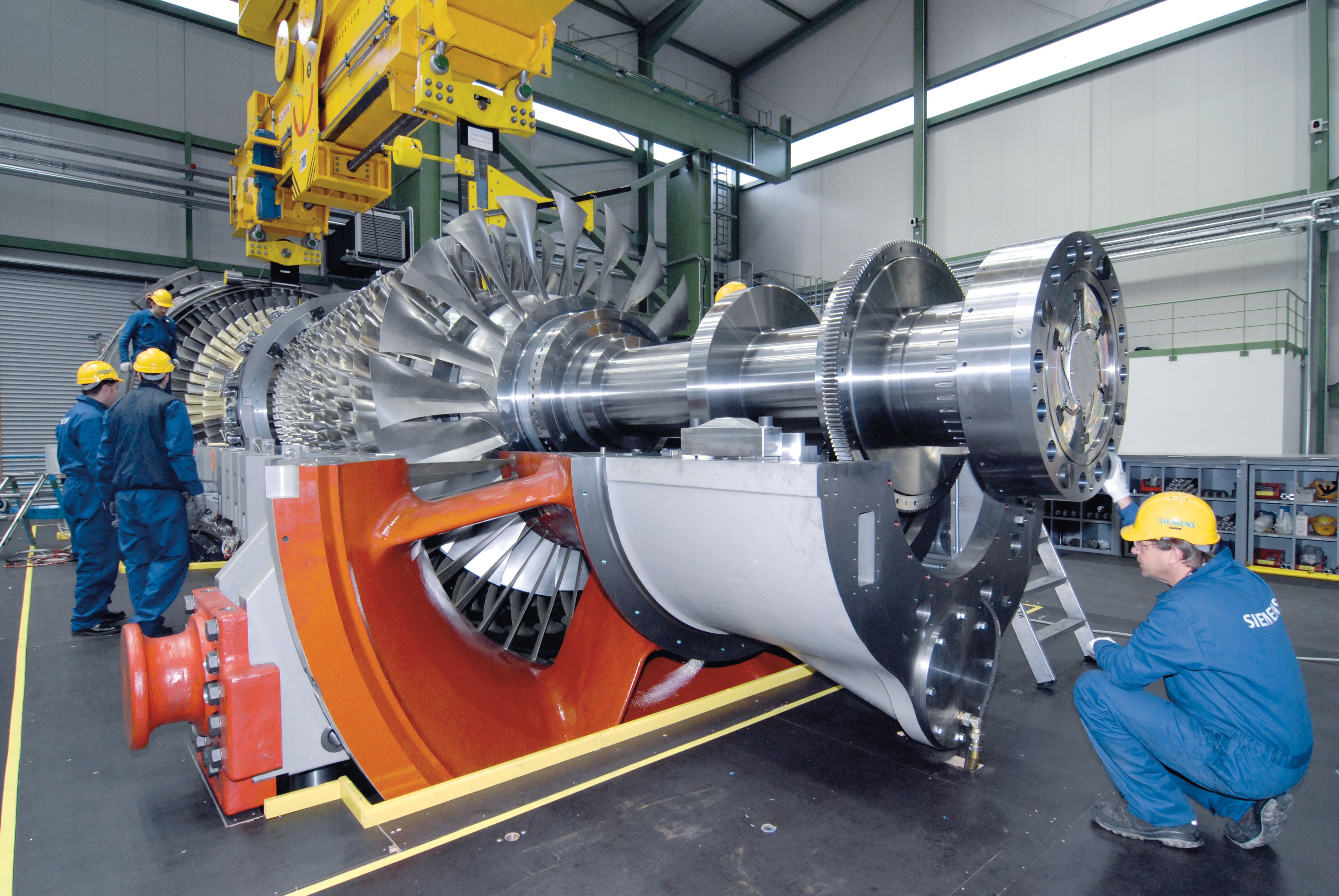

توربین گازی چگونه کار میکند؟
توربین گازی یک موتور حرارتی است که انرژی شیمیایی سوخت را به انرژی مکانیکی تبدیل میکند. این فرآیند شامل سه مرحله اصلی است: فشردهسازی هوا، احتراق سوخت و انبساط گازهای داغ. در مرحله اول، هوا توسط کمپرسور فشرده شده و وارد محفظه احتراق میشود. در مرحله دوم، سوخت به هوا اضافه شده و مخلوط سوخت و هوا در محفظه احتراق سوزانده میشود. گازهای داغ حاصل از احتراق با فشار بالا به سمت توربین هدایت میشوند. در مرحله سوم، گازهای داغ با عبور از پرههای توربین، باعث چرخش آن میشوند. انرژی مکانیکی حاصل از چرخش توربین میتواند برای تولید برق توسط ژنراتور یا برای به حرکت درآوردن سایر تجهیزات استفاده شود.
اجزای اصلی توربین گازی:
توربین گازی از اجزای مختلفی تشکیل شده است که هر کدام وظیفه خاصی را بر عهده دارند. اجزای اصلی توربین گازی عبارتند از:
- کمپرسور: وظیفه فشردهسازی هوا را بر عهده دارد. کمپرسورها معمولاً از نوع محوری یا گریز از مرکز هستند.
- محفظه احتراق: وظیفه سوزاندن مخلوط سوخت و هوا را بر عهده دارد. محفظههای احتراق باید به گونهای طراحی شوند که احتراق کامل و پایدار صورت گیرد.
- توربین: وظیفه تبدیل انرژی حرارتی گازهای داغ به انرژی مکانیکی را بر عهده دارد. توربینها معمولاً از چندین ردیف پره تشکیل شدهاند که به صورت متوالی قرار گرفتهاند.
- سیستم سوخترسانی: وظیفه تامین سوخت مورد نیاز برای احتراق را بر عهده دارد. سیستم سوخترسانی باید قادر باشد سوخت را با فشار و دبی مناسب به محفظه احتراق برساند.
- سیستم کنترل: وظیفه کنترل و نظارت بر عملکرد توربین گازی را بر عهده دارد. سیستم کنترل باید قادر باشد پارامترهای مختلف توربین گازی را اندازهگیری و تنظیم کند.
مطالعه مقاله: تجهیزات برق صنعتی در نیروگاههای برق بادی و توربینهای بادی
نیروگاههای برق بادی به عنوان یکی از منابع اصلی تولید انرژی تجدیدپذیر در جهان شناخته میشوند. با توجه به افزایش نگرانیها درباره تغییرات اقلیمی و کاهش منابع سوختهای فسیلی، استفاده از انرژی بادی به شدت مورد توجه قرار گرفته است. ادامه مطلب...
کاربردهای توربین گازی:
توربینهای گازی در صنایع مختلف کاربرد گستردهای دارند. برخی از کاربردهای اصلی توربینهای گازی عبارتند از:
- تولید برق: توربینهای گازی به عنوان یکی از اصلیترین مولدهای برق در نیروگاههای گازی و سیکل ترکیبی استفاده میشوند.
- صنایع نفت و گاز: توربینهای گازی برای به حرکت درآوردن کمپرسورها، پمپها و سایر تجهیزات در صنایع نفت و گاز استفاده میشوند.
- صنایع هوافضا: توربینهای گازی به عنوان موتور جت در هواپیماها و هلیکوپترها استفاده میشوند.
- صنایع دریایی: توربینهای گازی برای به حرکت درآوردن کشتیها و قایقها استفاده میشوند.
- تولید همزمان برق و حرارت (CHP): توربینهای گازی میتوانند برای تولید همزمان برق و حرارت مورد نیاز صنایع و ساختمانها استفاده شوند. سیستمهای CHP با افزایش راندمان و کاهش مصرف انرژی، به کاهش هزینهها و حفظ محیط زیست کمک میکنند.
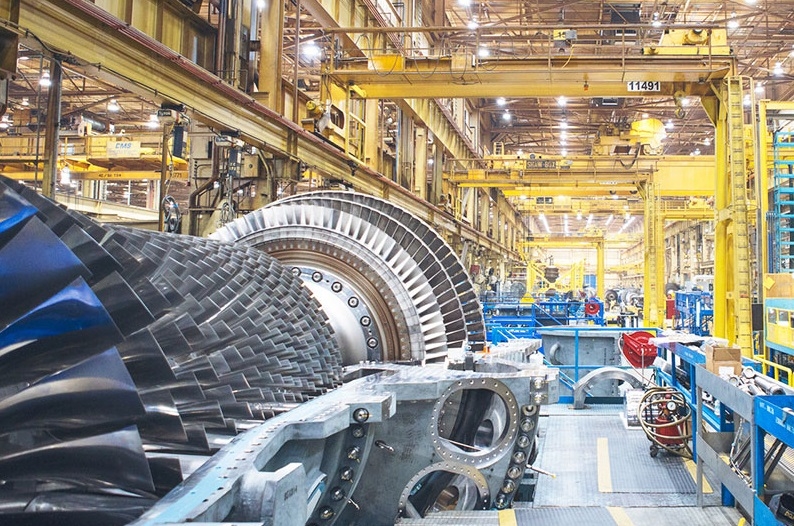

مزایای توربین گازی:
توربینهای گازی دارای مزایای متعددی هستند که آنها را به یک گزینه جذاب در بسیاری از کاربردها تبدیل کرده است. برخی از مزایای اصلی توربینهای گازی عبارتند از:
- راندمان بالا: توربینهای گازی سیکل ترکیبی میتوانند راندمانی بیش از 60 درصد داشته باشند.
- قابلیت اطمینان: توربینهای گازی به دلیل طراحی ساده و استفاده از مواد با کیفیت بالا، دارای قابلیت اطمینان بالایی هستند.
- انعطافپذیری در استفاده از سوخت: توربینهای گازی میتوانند از سوختهای مختلفی مانند گاز طبیعی، گازوئیل و سوختهای زیستی استفاده کنند.
- وزن و حجم کم: توربینهای گازی نسبت به سایر موتورهای حرارتی، دارای وزن و حجم کمتری هستند.
- زمان راهاندازی سریع: توربینهای گازی میتوانند در مدت زمان کوتاهی راهاندازی شده و به توان نامی برسند.
- کاهش آلایندگی: استفاده از فناوریهای احتراق پیشرفته و سیستمهای کاهش آلایندگی میتواند به کاهش انتشار گازهای مضر از توربینهای گازی کمک کند.
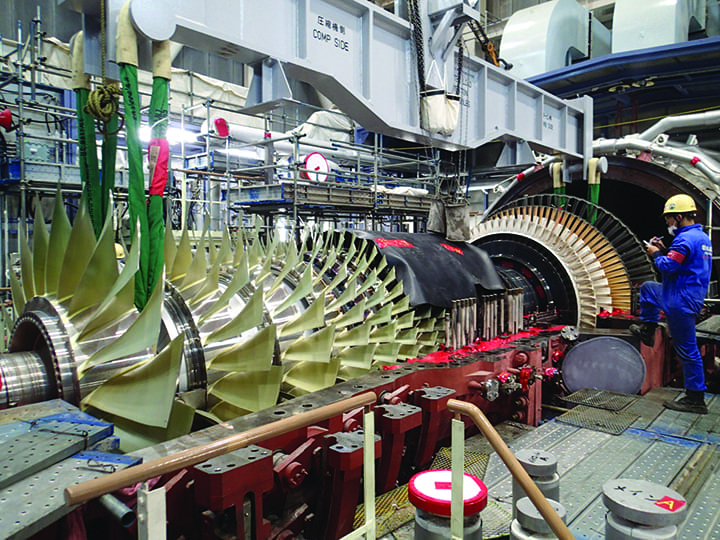
معایب توربین گازی:
در کنار مزایای فراوان، توربینهای گازی معایبی نیز دارند که باید در نظر گرفته شوند. برخی از معایب اصلی توربینهای گازی عبارتند از:
- هزینه اولیه بالا: هزینه خرید و نصب توربینهای گازی معمولاً بالا است.
- نیاز به نگهداری و تعمیرات منظم: توربینهای گازی نیاز به نگهداری و تعمیرات دورهای دارند تا عملکرد صحیح آنها تضمین شود.
- حساسیت به کیفیت سوخت: توربینهای گازی به کیفیت سوخت حساس هستند و استفاده از سوخت نامناسب میتواند باعث آسیب رسیدن به قطعات شود.
- آلودگی صوتی: توربینهای گازی در حین کارکرد صدای زیادی تولید میکنند که میتواند باعث ایجاد مزاحمت برای ساکنان مناطق مسکونی شود.
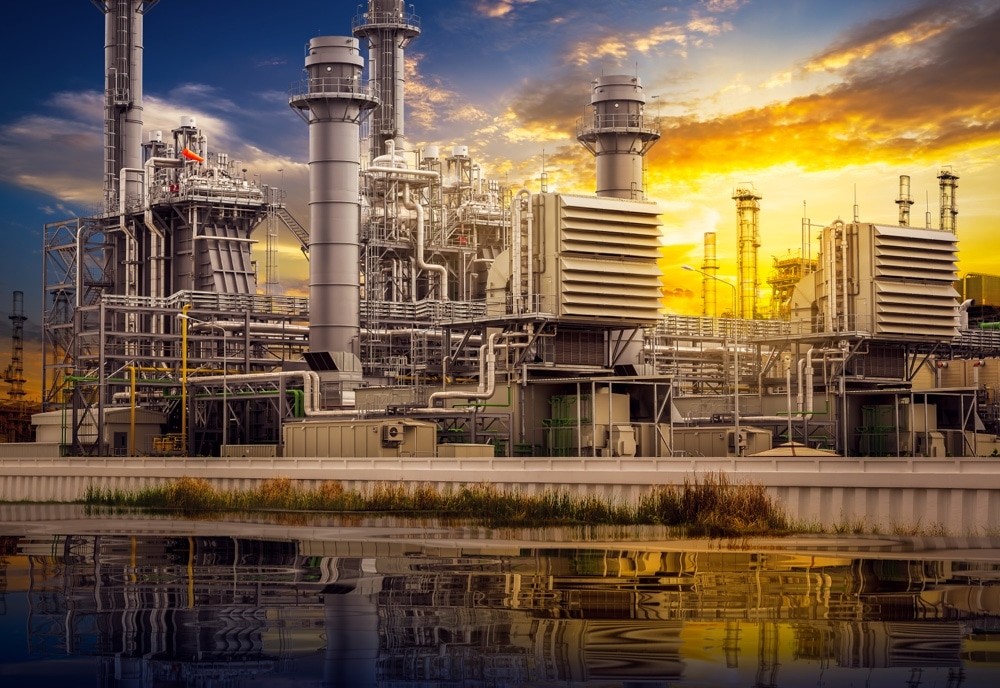

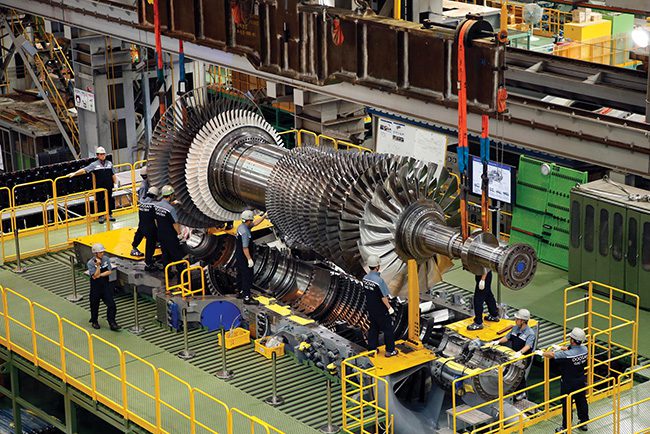
انواع توربین گازی:
توربینهای گازی بر اساس کاربرد و طراحی به انواع مختلفی تقسیم میشوند. برخی از انواع اصلی توربینهای گازی عبارتند از:
- توربین گازی صنعتی: برای کاربردهای ثابت مانند تولید برق و صنایع فرآیندی طراحی شده است.
- توربین گازی هواپیمایی: برای استفاده در هواپیماها و هلیکوپترها طراحی شده است.
- میکروتوربین گازی: در ابعاد کوچک و برای تولید برق در مقیاس کوچک طراحی شده است.
- توربین گازی دریایی: برای استفاده در کشتیها و قایقها طراحی شده است.
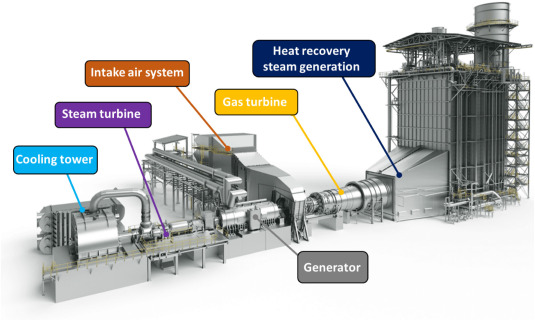
نقش توربین گازی در برق صنعتی:
در بخش برق صنعتی، توربینهای گازی نقش بسیار مهمی در تامین انرژی مورد نیاز صنایع بزرگ و کوچک دارند. استفاده از توربینهای گازی در صنایع میتواند مزایای متعددی از جمله کاهش هزینههای انرژی، افزایش قابلیت اطمینان سیستمهای تولید برق و کاهش آلایندگی را به همراه داشته باشد. همچنین، استفاده از سیستمهای CHP مبتنی بر توربین گازی میتواند به بهرهوری بیشتر انرژی و کاهش هزینههای تولید کمک کند. در صنایع بزرگ مانند صنایع فولاد، سیمان و پتروشیمی، توربینهای گازی به عنوان یکی از اصلیترین منابع تولید برق و حرارت مورد استفاده قرار میگیرند.

چالشها و راهکارهای پیش روی توربینهای گازی:
صنعت توربین گازی با چالشهای مختلفی از جمله افزایش راندمان، کاهش آلایندگی و استفاده از سوختهای جایگزین روبرو است. برای مقابله با این چالشها، تحقیقات و توسعههای گستردهای در حال انجام است. برخی از راهکارهای کلیدی برای بهبود عملکرد و کاهش آلایندگی توربینهای گازی عبارتند از:
- بهینهسازی طراحی و مواد: استفاده از مواد پیشرفته و طراحی بهینه قطعات میتواند به افزایش راندمان و عمر مفید توربینهای گازی کمک کند.
- توسعه سیستمهای احتراق پیشرفته: استفاده از سیستمهای احتراق کم NOx و Lean Premixed Combustion میتواند به کاهش انتشار گازهای مضر کمک کند.
- استفاده از سیستمهای بازیابی حرارت: استفاده از سیستمهای بازیابی حرارت اتلافی میتواند به افزایش راندمان کلی سیستم کمک کند.
- استفاده از سوختهای جایگزین: استفاده از سوختهای تجدیدپذیر مانند بیوگاز و هیدروژن میتواند به کاهش وابستگی به سوختهای فسیلی کمک کند.
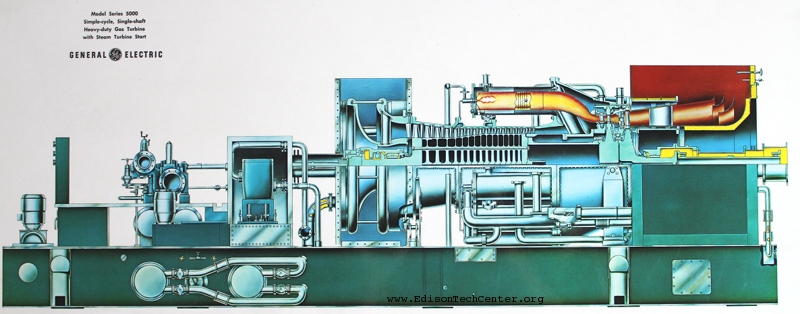
نگهداری و تعمیرات توربین گازی:
نگهداری و تعمیرات دورهای توربین گازی برای اطمینان از عملکرد صحیح و افزایش عمر مفید آن ضروری است. این فعالیتها شامل بازرسیهای منظم، تعویض قطعات فرسوده و انجام تعمیرات اساسی در صورت نیاز میشود. برنامههای نگهداری پیشگیرانه (Preventive Maintenance) و پایش وضعیت (Condition Monitoring) میتوانند به شناسایی زودهنگام مشکلات و جلوگیری از خرابیهای ناگهانی کمک کنند.
روندهای نوین و آینده توربینهای گازی:
صنعت توربین گازی به طور مداوم در حال توسعه و نوآوری است. روندهای نوین در این حوزه شامل افزایش راندمان، کاهش آلایندگی، استفاده از سوختهای تجدیدپذیر و توسعه توربینهای گازی هیبریدی است. استفاده از فناوریهای پیشرفته مانند سیکلهای ترکیبی، خنککاری پیشرفته پرهها و سیستمهای احتراق کم NOx میتواند به افزایش راندمان و کاهش آلایندگی توربینهای گازی کمک کند. همچنین، استفاده از سوختهای تجدیدپذیر مانند بیوگاز و هیدروژن میتواند به کاهش وابستگی به سوختهای فسیلی و کاهش انتشار گازهای گلخانهای کمک کند. در زمینه برق صنعتی، توسعه سیستمهای کنترل هوشمند و استفاده از اینترنت اشیا (IoT) میتواند به بهبود عملکرد و افزایش قابلیت اطمینان توربینهای گازی کمک کند.
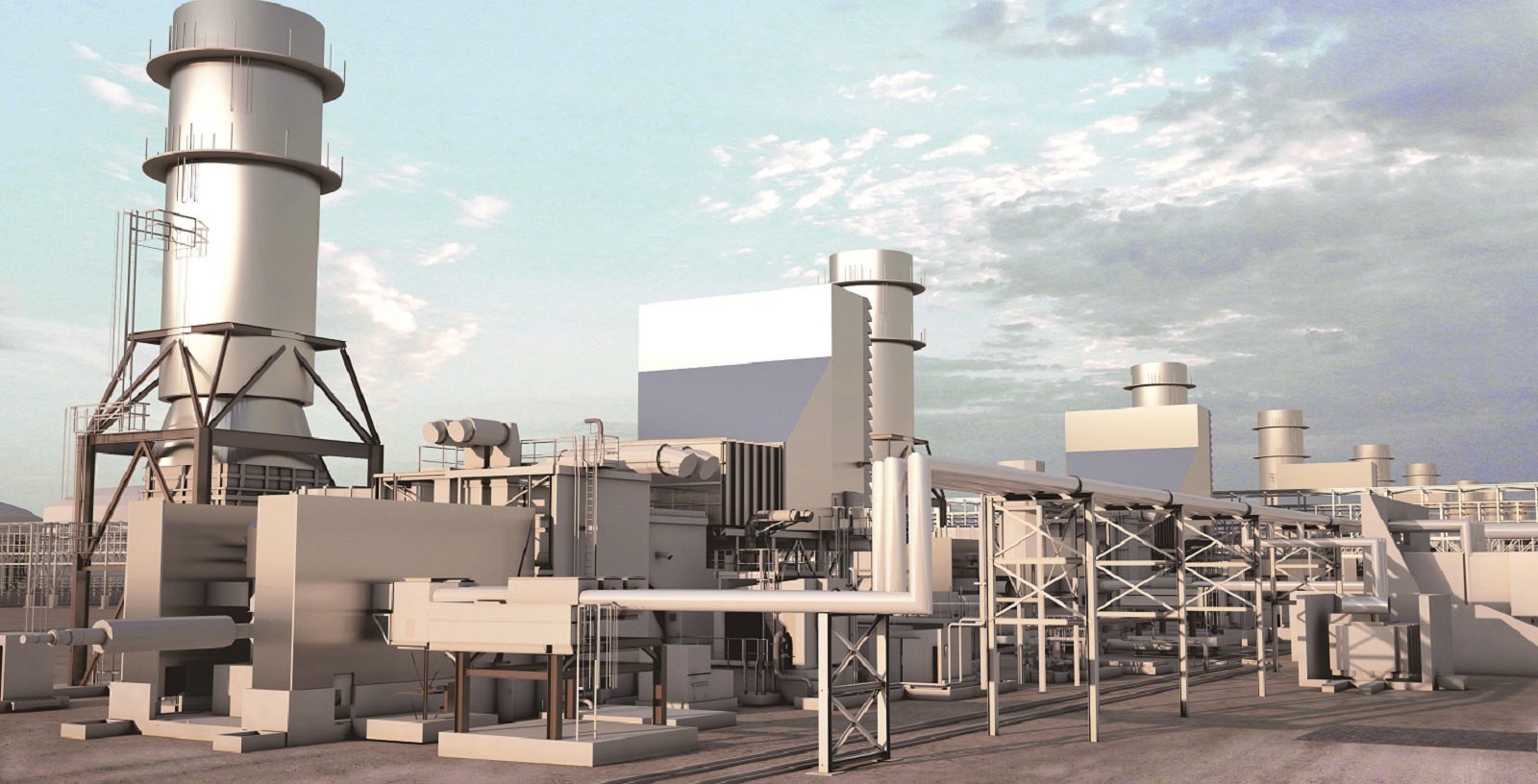

نتیجهگیری:
توربین گازی به عنوان یک فناوری کلیدی در صنعت انرژی، نقش مهمی در تولید برق، تامین حرارت و به حرکت درآوردن تجهیزات مختلف ایفا میکند. با توجه به مزایای این فناوری و پیشرفتهای صورت گرفته در زمینه افزایش راندمان و کاهش آلایندگی، انتظار میرود که توربینهای گازی همچنان نقش مهمی در آینده انرژی جهان داشته باشند. توسعه و بهینهسازی توربینهای گازی، با هدف افزایش راندمان، کاهش آلایندگی و استفاده از سوختهای تجدیدپذیر، میتواند به تامین انرژی پایدار و کاهش وابستگی به سوختهای فسیلی کمک کند. در حوزه برق صنعتی، استفاده از توربینهای گازی به عنوان یک منبع تولید برق قابل اعتماد و کارآمد، نقش مهمی در تامین انرژی مورد نیاز صنایع و کاهش هزینههای تولید ایفا میکند.
Gas Turbine: The Beating Heart of Industries, Power Plants, and Its Role in Industrial Electricity
Keywords
Gas turbine, gas power plant, electricity generation, compressor, combustion chamber, gas turbine efficiency, gas turbine maintenance, gas turbine applications, gas turbine types, industrial electricity, CHP system, combined heat and power generation, high-efficiency gas turbine, gas turbine emission reduction, alternative fuel gas turbine
Abstract
Gas turbines, as one of the most important power generators in various industries, play a key role in electricity generation and energy supply. This article provides a comprehensive review of the performance, components, applications, advantages, and disadvantages of gas turbines. It also examines the latest trends and the future of this technology, particularly in the field of industrial electricity and combined heat and power (CHP) generation. The aim of this article is to provide a complete and up-to-date perspective on gas turbines and their role in the energy industry
Introduction
In today's world, energy, as one of the most basic human needs, plays a vital role in economic and social development. Gas turbines, as one of the most important sources of energy production, are widely used in various industries, including power plants, oil and gas industries, and aerospace. These powerful machines, by converting the energy from fuel combustion into mechanical energy, enable the production of electricity, the movement of equipment, and the supply of heat required by industries. Gas turbines have become an attractive option for energy production due to their advantages such as high efficiency, reliability, and flexibility in the use of various fuels
How Does a Gas Turbine Work
A gas turbine is a heat engine that converts the chemical energy of fuel into mechanical energy. This process involves three main stages: air compression, fuel combustion, and expansion of hot gases. In the first stage, air is compressed by the compressor and enters the combustion chamber. In the second stage, fuel is added to the air, and the fuel-air mixture is burned in the combustion chamber. The hot gases from the combustion are directed to the turbine at high pressure. In the third stage, the hot gases pass through the turbine blades, causing it to rotate. The mechanical energy from the turbine rotation can be used to generate electricity by a generator or to power other equipment
Main Components of a Gas Turbine
A gas turbine consists of various components, each of which has a specific function. The main components of a gas turbine include
- Compressor: Responsible for compressing the air. Compressors are usually of the axial or centrifugal type
- Combustion Chamber: Responsible for burning the fuel-air mixture. Combustion chambers must be designed to ensure complete and stable combustion
- Turbine: Responsible for converting the thermal energy of hot gases into mechanical energy. Turbines usually consist of several rows of blades arranged in series
- Fuel Supply System: Responsible for supplying the fuel required for combustion. The fuel supply system must be able to deliver fuel to the combustion chamber at the appropriate pressure and flow rate
- Control System: Responsible for controlling and monitoring the performance of the gas turbine. The control system must be able to measure and adjust various parameters of the gas turbine
Applications of Gas Turbines
Gas turbines have a wide range of applications in various industries. Some of the main applications of gas turbines include
- Electricity Generation: Gas turbines are used as one of the main generators of electricity in gas and combined cycle power plants
- Oil and Gas Industries: Gas turbines are used to drive compressors, pumps, and other equipment in the oil and gas industries
- Aerospace: Gas turbines are used as jet engines in airplanes and helicopters
- Marine Industries: Gas turbines are used to power ships and boats
- Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Generation: Gas turbines can be used to generate electricity and heat required by industries and buildings simultaneously. CHP systems help reduce costs and protect the environment by increasing efficiency and reducing energy consumption
Advantages of Gas Turbines
Gas turbines have several advantages that make them an attractive option in many applications. Some of the main advantages of gas turbines include
- High Efficiency: Combined cycle gas turbines can have an efficiency of over 60%
- Reliability: Gas turbines are highly reliable due to their simple design and the use of high-quality materials
- Fuel Flexibility: Gas turbines can use various fuels such as natural gas, diesel, and biofuels
- Low Weight and Volume: Gas turbines have lower weight and volume compared to other heat engines
- Fast Startup Time: Gas turbines can be started in a short time and reach rated power
- Emission Reduction: The use of advanced combustion technologies and emission reduction systems can help reduce the emission of harmful gases from gas turbines
Disadvantages of Gas Turbines
In addition to their numerous advantages, gas turbines also have disadvantages that should be considered. Some of the main disadvantages of gas turbines include
- High Initial Cost: The cost of purchasing and installing gas turbines is usually high
- Regular Maintenance and Repairs: Gas turbines require regular maintenance and repairs to ensure their proper performance
- Sensitivity to Fuel Quality: Gas turbines are sensitive to fuel quality, and the use of unsuitable fuel can damage components
- Noise Pollution: Gas turbines produce a lot of noise during operation, which can be a nuisance to residents of residential areas
Types of Gas Turbines
Gas turbines are divided into different types based on application and design. Some of the main types of gas turbines include
- Industrial Gas Turbine: Designed for stationary applications such as power generation and process industries
- Aviation Gas Turbine: Designed for use in airplanes and helicopters
- Micro Gas Turbine: Designed in small dimensions for small-scale electricity generation
- Marine Gas Turbine: Designed for use in ships and boats
The Role of Gas Turbines in Industrial Electricity
In the industrial electricity sector, gas turbines play a very important role in supplying the energy needs of large and small industries. The use of gas turbines in industries can have several advantages, including reducing energy costs, increasing the reliability of electricity generation systems, and reducing emissions. Also, the use of CHP systems based on gas turbines can help increase energy efficiency and reduce production costs. In large industries such as steel, cement, and petrochemical industries, gas turbines are used as one of the main sources of electricity and heat production
Challenges and Solutions for Gas Turbines
The gas turbine industry faces various challenges, including increasing efficiency, reducing emissions, and using alternative fuels. To address these challenges, extensive research and development is underway. Some of the key solutions to improve the performance and reduce
emissions of gas turbines include
- Optimization of Design and Materials: The use of advanced materials and optimized component design can help increase the efficiency and service life of gas turbines
- Development of Advanced Combustion Systems: The use of low NOx and Lean Premixed Combustion systems can help reduce the emission of harmful gases
- Use of Heat Recovery Systems: The use of waste heat recovery systems can help increase the overall system efficiency
- Use of Alternative Fuels: The use of renewable fuels such as biogas and hydrogen can help reduce dependence on fossil fuels
Gas Turbine Maintenance and Repairs
Regular maintenance and repairs of gas turbines are necessary to ensure proper operation and increase their service life. These activities include regular inspections, replacement of worn parts, and major repairs as needed. Preventive maintenance programs and condition monitoring can help identify problems early and prevent sudden failures
New Trends and the Future of Gas Turbines
The gas turbine industry is constantly evolving and innovating. New trends in this area include increasing efficiency, reducing emissions, using renewable fuels, and developing hybrid gas turbines. The use of advanced technologies such as combined cycles, advanced blade cooling, and low NOx combustion systems can help increase the efficiency and reduce the emissions of gas turbines. Also, the use of renewable fuels such as biogas and hydrogen can help reduce dependence on fossil fuels and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. In the field of industrial electricity, the development of intelligent control systems and the use of the Internet of Things (IoT) can help improve the performance and increase the reliability of gas turbines
Conclusion
Gas turbines, as a key technology in the energy industry, play an important role in electricity generation, heat supply, and driving various equipment. Given the advantages of this technology and the advances made in increasing efficiency and reducing emissions, gas turbines are expected to continue to play an important role in the future of the world's energy. The development and optimization of gas turbines, with the aim of increasing efficiency, reducing emissions, and using renewable fuels, can help provide sustainable energy and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. In the field of industrial electricity, the use of gas turbines as a reliable and efficient source of electricity generation plays an important role in supplying the energy needs of industries and reducing production costs
References
- Boyce, M. P. (2006). Gas Turbine Engineering Handbook. Gulf Professional Publishing.
- Lefebvre, A. H., & Ballal, D. R. (2010). Gas Turbine Combustion: Alternative Fuels and Emissions. CRC press.
- Kehlhofer, R., Bachmann, R., Nielsen, H., & Warner, J. (2009). Combined-Cycle Gas & Steam Turbine Power Plants. PennWell Books.
- Smith, D. J. (2014). *Reliability, Maintainability






